Getting Started
4D View Pro is a 4D component that includes a 4D form area and specific commands. It allows you to embed advanced spreadsheet features in your projects.
A spreadsheet is an application containing a grid of cells into which you can enter information, execute calculations, or display pictures. 4D View Pro is powered by the SpreadJS spreadsheet solution integrated in 4D.
Embedding 4D View Pro areas in your forms allows you to import and export spreadsheets documents using the 4D View Pro commands.
Installation and activation
4D View Pro features are directly included in 4D, making it easy to deploy and manage. No additional installation is required.
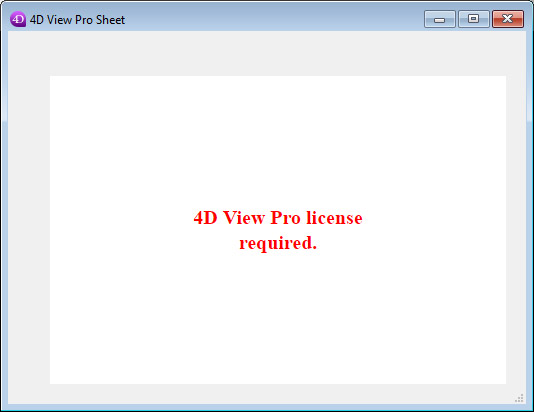
However, 4D View Pro requires a license. You need to activate this license in your application in order to use its features. When using this component without a license, the contents of an object that requires a 4D View Pro feature are not displayed at runtime, an error message is displayed instead:
SapphireOne license includes 4D View Pro and 4D Write Pro
Inserting a 4D View Pro area
4D View Pro documents are displayed and edited manually in a 4D form object named 4D View Pro. To select this object, click on the last tool in the object bar:
You can also select a preconfigured 4D View Pro area in the Object library.
4D View Pro areas can also be created and used offscreen.
You can configure the area using the Property List and 4D View Pro methods.
Selection, Input and Navigation Basics
Spreadsheets are composed of rows and columns. A number is associated with each row. A letter (or group of letters once the number of columns surpasses the number of letters in the alphabet) is associated with each column. The intersection of a row and a column makes a cell. Cells can be selected and their contents edited.
Selecting cells, columns and rows
- To select a cell, simply click on it or use the direction arrows on the keyboard. Its content (or formula) is displayed within the cell.
- To select several continuous cells, drag the mouse from one end of the selection to the other. You can also click on the two ends of the selection while holding down the Shift key.
- To select all cells in the spreadsheet, click on the cell at the top left of the area:

- To select a column, click on the corresponding letter (or set of letters).
- To select a row, click on the corresponding number.
- To select a group of cells that are not continuous, hold down the Ctrl key (Windows) or Command key (Mac) and click on each cell to be selected.
- To deselect cells, simply click anywhere within the spreadsheet.
Entering data
Double-clicking on a cell allows passing into input mode in the relevant cell. If the cell is not empty, the insertion cursor is placed after the content of the cell.
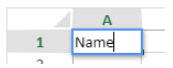
Data can be entered directly once a cell is already selected, even if the insertion cursor is not visible. The input then replaces the content of the cell.
The Tab key validates the cell input and selects the cell to its right. Combining the Shift + Tab keys validates the cell input and selects the cell to its left.
The Carriage return key validates the cell input and selects the cell below it. Combining the Shift + Carriage return keys validates the cell input and selects the cell above it.
The direction keys (arrows) allow you to move a cell in the direction indicated by the arrow.
Using the Context Menu
4D View Pro areas benefit from an automatic context menu that offers standard editing features such as copy and paste, but also basic spreadsheet features:
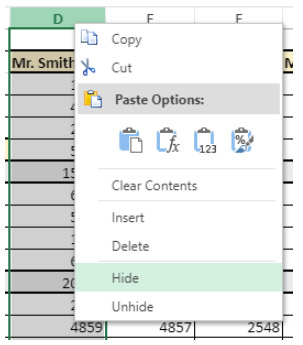
The Copy/Cut and Paste features of the context menu only work within the spreadsheet area, they do not have access to the system pasteboard. System shortcuts such as Ctrl+c/Ctrl+vworks however and can be used to exchange data between the area and other applications.
Depending on the clicked area, the following options are also available:
- click on a column or row header: Insert, Delete, Hide, or Unhidethe contents
- click on a cell or a cell range:
- Filter: allows hiding row through filters (see Filtering rows in the SpreadJS documentation).
- Sort: sorts the column contents.
- Insert Comment: allows user to enter a comment for an area. When a comment has been entered for an area, the top left cell of the area displays a small red triangle:

Using 4D View Pro methods
4D View Pro methods can be used in the 4D Code Editor, just like 4D language commands.
Since 4D View Pro is a built-in 4D component, you can access its list of methods from the Explorer, in the Component Methods section:
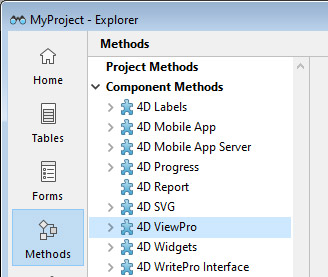
For a detailed list of component methods, see Method list.
Import From a SapphireOne Inquiry
The values of all cells from any SapphireOne inquiry can be imported into a 4D View Pro document with ease. The procedure is as follows.
- Open any SapphireOne Inquiry. Either standard or custom.
- Select 4D View Pro from the Sapphire Tools menu.
- Select the
 Import From Inquiry button on the bottom left corner of the 4D View Pro screen.
Import From Inquiry button on the bottom left corner of the 4D View Pro screen.
In SapphireOne, all inquiry screens provide the option for customisation of the displayed item list. The feature, called Custom Inquiry, lets users choose the data fields to be shown and the sequence of data columns across the screen. The user can save infinite custom views. While a client list is used as an example to follow, any inquiry type can be customised in SapphireOne.
The Standard Inquiry Screen
The Standard Inquiry Screen in SapphireOne provides a foundational view of data, presenting a set of column fields for each record. This screen is designed to offer a straightforward and efficient way to access and review essential information.
The list above represents the standard inquiry list, displaying a fundamental set of data fields for each client record and includes two buttons as follows:
- Swap to Custom Inquiry – When the user selects the ‘Swap to Custom Inquiry’ button in the lower left-hand corner of the screen, SapphireOne will display the default Custom Inquiry Screen, which is documented below.
- Show/Hide Audit Lines – Toggle the Audit lines panel open. This panel will display at the bottom of the Inquiry screen, benefiting workflow by providing an immediate view of the critical details for a selected line.
The Custom Inquiry Screen
When the user selects the ‘Swap to Custom Inquiry’ button from the Standard Inquiry, SapphireOne will display the default Custom Inquiry Screen, as shown below. This screen provides the user with a customisable view of the data set, which is maintained per user and for each particular inquiry.
The options available from the Custom Inquiry Screen are as follows:
- Swap to Standard Inquiry – Return the view to a standard Inquiry.
- Method List Box – This list box, in conjunction with the adjacent operator list box, allows for calculations to be performed across all rows of the displayed data. The results are displayed adjacent to the operator list box.
- Operator List Box – Select an operator to apply to the method selected using the method list box.
- Setup Button – The Setup button will open a modal screen with functionality to customise the Custom Inquiry, as documented in the following section.
- Export Button – Open the data set in CSV format in the devices default spreadsheet application.
The Custom Inquiry Setup Screen
The Custom Inquiry setup screen allows for the customisation of the data view, which is maintained per user and for each particular inquiry. Once the user has customised the Custom Inquiry screen, the screen view will be maintained in subsequent sessions and is unique to the current user account. This screen also provides the option to select and save an unlimited number of custom views per user.
The Custom Inquiry setup screen provides the following functionality:
- Favourite Sets – This option enables the user to save a custom-created screen for future use. For instance, the user can have a simple Inquiry screen for general use and a more complex screen view when auditing specific information.
- Row Height – Adjust the table row height to the users preference.
- Show Related Record – This option allows the user to add related fields from other tables. By ticking the Show Related checkbox at the top of the screen, the user can select a related record, and a view of that related record for the chosen entry will be displayed for that currently selected record. The user will need to select the fields to be displayed.
- Reset to Default – Reset the display to the default view configuration as established by SapphireOne.
The Custom Inquiry setup screen provides the user with two main options for organising the data displayed:
- To remove or relocate a column – Right-click on the column lines and choose from Delete, Move Left, or Move Right.
- To add a column – Locate the desired data set in the list and double-click on it to add it to the custom view as a new column. Edit the location as described above if required. Almost every field within the SapphireOne data tables can be included in the Custom List screen, provided the user has the necessary authorisation.
Customising inquiry screens in SapphireOne allows for a tailored data view that meets the users specific needs. By leveraging the Custom Inquiry feature, the user can enhance their workflow efficiency and ensure that critical information is readily accessible.
Addressing a 4D View Pro area
A 4D View Pro area handles several objects and elements.
Most of 4D View Pro methods require a vpAreaName parameter, which is the 4D View Pro form area name (4D form object). This name is the object name property.
For example, if you want to set the total number of columns of an area named “myVpArea”, you write:
VP SET COLUMN COUNT("myVpArea";5)When loading a 4D View Pro object in a form area, 4D generates the On VP Ready form event once the whole area is loaded. You must execute any 4D View Pro code handling the area in this event, otherwise an error is returned.
Using range objects
Some 4D View Pro methods require a rangeObj parameter. In 4D View Pro, a range is an object that references an area in a spreadsheet. This area can be composed of one or several cells. Using 4D View Pro methods, you can create ranges and pass them to other methods to read from or write to specific locations in your document.
For example, to create a range object for the following cells:
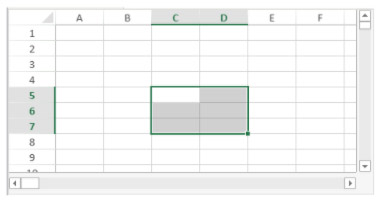
You can use the VP Cells method:
var $myRange : Object
$myRange:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";2;4;2;3) // C5 to D7You can then pass $myRange to another 4D View Pro method to modify these cells (for example add a border to the set of cells with VP SET BORDER).
4D View Pro range objects are composed of several properties:
- area – The name of the 4D View Pro area
- ranges – A collection of range object(s). Available properties within each range object depend on the range object type. For example, a column range object will only include the .column and .sheet properties.
| Property | Type | Description | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| area | text | 4D View Pro area form object name | always available | |
| ranges | collection | Collection of range(s) | always available | |
| [ ].name | text | Range name | name | |
| [ ].sheet | number | Sheet index (current sheet index by default) (counting begins at 0) | cell, cells, row, rows, column, columns, all, name | |
| [ ].row | number | Row index (counting begins at 0) | cell, cells, row, rows | |
| [ ].rowCount | number | Row count | cells, rows | |
| [ ].column | number | Column index (counting begins at 0) | cell, cells, column, columns | |
| [].columnCount | number | Column count | cells, columns |
Importing and exporting documents
4D View Pro supports the import and export of several document formats:
- .4vp
- .xlsx
- .txt and .csv
- .pdf (for export only)
For more details, check out the description of VP IMPORT DOCUMENTand VP EXPORT DOCUMENT.
Configuring 4D View Pro Areas
The 4D View Pro area properties can be configured using the Property list. Spreadsheet properties are available through the language.
Form area properties
Using the area’s property list, you can set 4D View Pro object properties such as Object Name, Variable or Expression, Appearance, Action, and Events.
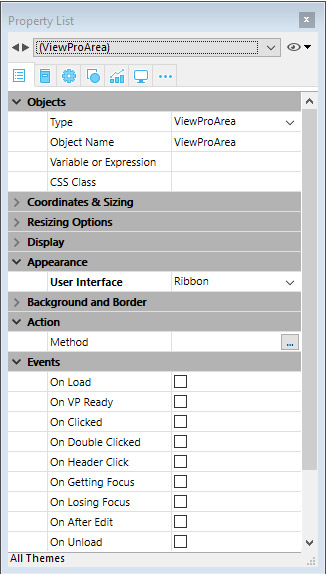
Selecting a user interface
You can select the interface to use with your 4D View Pro form areas in the Property List, under Appearance:
You can also use the
userInterfaceandwithFormulaBar(only with the “toolbar” interface) JSON properties.
Interfaces allow for basic modifications and data manipulation. User-defined modifications are saved in the 4D View Pro object when the user saves the document.
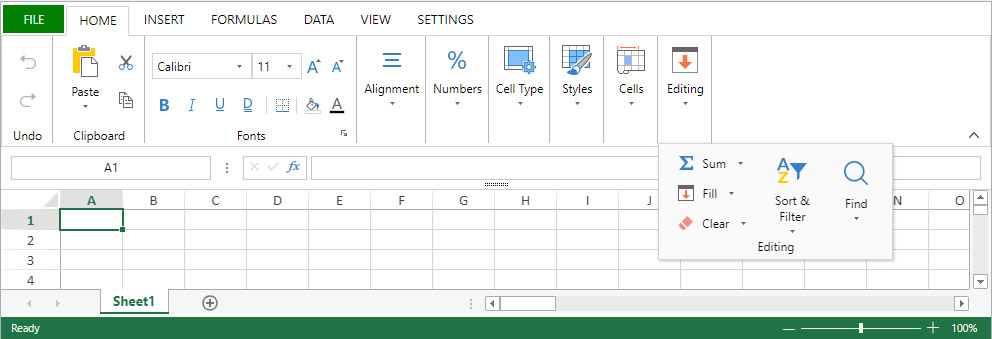
Ribbon
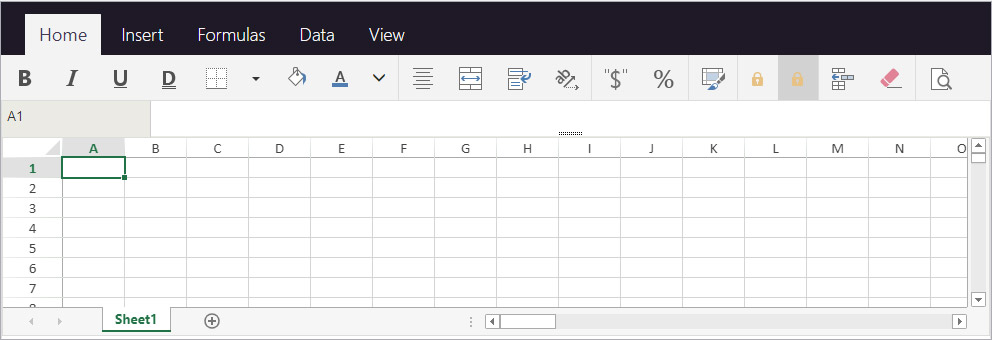
Toolbar
Enabling the Toolbar interface displays the Show Formula Bar option. When selected, the formula bar is visible below the Toolbar interface.
With visible formula bar:
Features
Both the Ribbon and the Toolbar interfaces group related features into tabs:
| Tab | Actions | Ribbon Interface | Toolbar Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| File | File manipulation | X | |
| Home | Text appearance | X | X |
| Insert | Add items | X | X |
| Formulas | Formula calculation and library | X | X |
| Data | Data manipulation | X | X |
| View | Visual presentation | X | X |
| Settings | Sheet presentation reference | X |
Form Events
The following form events are available in the Property List for 4D View Pro areas.
Some of the events are standard form events (available to all active objects) and some are specific 4D View Pro form events. Some standard form events provide extended information in the object returned by the FORM Event command when they are generated for 4D View Pro areas. The following table shows which events are standard and which are specific or provide additional information to 4D View Pro areas:
| Standard 4D events | Specific and extended 4D View Pro events |
|---|---|
| On Load | On VP Ready |
| On Getting Focus | On Clicked |
| On Losing Focus | On Double Clicked |
| On Unload | On Header Click |
| On After Edit | |
| On Selection Change | |
| On Column Resize | |
| On Row Resize | |
| On VP Range Changed |
Sheet Options
The 4D View Pro sheet options object allows you to control various options of your 4D View Pro areas. This object is handled by the following commands:
Sheet appearance
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| allowCellOverflow | boolean | Specifies whether data can overflow into adjacent empty cells. | |
| sheetTabColor | string | A color string used to represent the sheet tab color, such as “red”, “#FFFF00”, “rgb(255,0,0)”, “Accent 5”, and so on. | |
| frozenlineColor | string | A color string used to represent the frozen line color, such as “red”, “#FFFF00”, “rgb(255,0,0)”, “Accent 5”, and so on. | |
| clipBoardOptions | longint | The clipboard option. Available values: vk clipboard paste options all, vk clipboard paste options formatting, vk clipboard paste options formulas, vk clipboard paste options formulas and formatting, vk clipboard paste options values, vk clipboard paste options values and formatting |
|
| gridline | object | The grid line’s options. | |
| color | string | A color string used to represent the grid line color, such as “red”, “#FFFF00”, “rgb(255,0,0)”, “Accent 5”, and so on. | |
| showVerticalGridline | boolean | Specifies whether to show the vertical grid line. | |
| showHorizontalGridline | boolean | Specifies whether to show the horizontal grid line. | |
| rowHeaderVisible | boolean | Specifies whether the row header is visible. | |
| colHeaderVisible | boolean | Specifies whether the column header is visible. | |
| rowHeaderAutoText | longint | Specifies whether the row header displays letters or numbers or is blank. Available values: vk header auto text blank, vk header auto text letters, vk header auto text numbers |
|
| colHeaderAutoText | longint | Specifies whether the column header displays letters or numbers or is blank. Available values: vk header auto text blank, vk header auto text letters, vk header auto text numbers |
|
| selectionBackColor | string | The selection’s background color for the sheet. (preferred RGBA format) | |
| selectionBorderColor | string | The selection’s border color for the sheet. | |
| sheetAreaOffset | object | The sheetAreaOffset’s options. | |
| left | longint | The offset left of sheet from host. | |
| top | longint | The offset top of sheet from host. |
All properties are optional.
Sheet protection
To lock the whole sheet, you only need to set the isProtected property to true. You can then unlock cells individually by setting the locked cell style property.
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| isProtected | boolean | Specifies whether cells on this sheet that are marked as protected cannot be edited. | |
| protectionOptions | object | A value that indicates the elements that you want users to be able to change. If null : the protectionOptions parameter is reset. | |
| allowSelectLockedCells | boolean | Specifies whether the user can select locked cells, optional. True by default. | |
| allowSelectUnlockedCells | boolean | Specifies whether the user can select unlocked cells, optional. True by default. | |
| allowSort | boolean | Specifies whether the user can sort ranges, optional. False by default. | |
| allowFilter | boolean | Specifies whether the user can filter ranges, optional. False by default. | |
| allowEditObjects | boolean | Specifies whether the user can edit floating objects, optional. False by default. | |
| allowResizeRows | boolean | Specifies whether the user can resize rows, optional. False by default. | |
| allowResizeColumns | boolean | Specifies whether the user can resize columns, optional. False by default. | |
| allowDragInsertRows | boolean | Specifies whether the user can perform the drag operation to insert rows, optional. False by default. | |
| allowDragInsertColumns | boolean | Specifies whether the user can perform the drag operation to insert columns, optional. False by default. | |
| allowInsertRows | boolean | Specifies whether the user can insert rows, optional. False by default. | |
| allowInsertColumns | boolean | Specifies whether the user can insert columns, optional. False by default. | |
| allowDeleteRows | boolean | Specifies whether the user can delete rows, optional. False by default. | |
| allowDeleteColumns | boolean | Specifies whether the user can delete columns, optional. False by default. |
All properties are optional.
Cell Format
Defining a format pattern ensures that the content of your 4D View Pro documents is displayed the way you intended. Formats can be set using the selected 4D View Pro interface, or using the VP SET VALUEor VP SET NUM VALUE methods.
4D View Pro has built-in formats for numbers, dates, times, and text, but you can also create your own patterns to format the contents of cells using special characters and codes.
For example, when using the VP SET VALUE or VP SET NUM VALUEmethods to enter amounts in an invoice, you may want the currency symbols ($, €, ¥, etc.) to be aligned regardless of the space required by the number (i.e., whether the amount is $5.00 or $5,000.00). You could use formatting characters and spectify the pattern ($* #,##0.00) which would display amounts as shown:
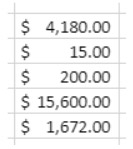
Note that when creating your own format patterns, only the display of the data is modified. The value of the data remains unchanged.
Number and text formats
Number formats apply to all number types (e.g., positive, negative, and zeros).
| Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Placeholder that displays zeros. | #.00 will display 1.1 as 1.10 |
| . | Displays a decimal point | 0.00 will display 1999 as 1999.00 |
| , | Displays the thousands separator in a number. Thousands are separated by commas if the format contains a comma enclosed by number signs “#” or by zeros. A comma following a digit placeholder scales the number by 1,000. | #,0 will display 12200000 as 12,200,000 |
| _ | Skips the width of the next character. | Usually used in combination with parentheses to add left and right indents, _( and _) respectively. |
| @ | Formatter for text. Applies the format to all text in the cell | “[Red]@” applies the red font color for text values. |
| * | Repeats the next character to fill the column width. | 0– will include enough dashes after a number to fill the cell, whereas 0 before any format will include leading zeros. |
| ” “ | Displays the text within the quotes without interpreting it. | “8%” will display as: 8% |
| % | Displays numbers as a percentage of 100. | 8% will be displayed as .08 |
| # | Digit placeholder that does not display extra zeros. If a number has more digits to the right of the decimal than there are placeholders, the number is rounded up. | #.# will display 1.54 as 1.5 |
| ? | Digit placeholder that leaves space for extra zeros, but does not display them. Typically used to align numbers by decimal point. | $?? displays a maximum of 2 decimals and causes dollar signs to line up for varying amounts. |
| \ | Displays the character following it. | #.00\? will display 123 as 123.00? |
| / | When used with numbers, displays them as fractions. When used with text, date or time codes, displayed “as-is”. | #/# will display .75 as 3/4 |
| [ ] | Creates conditional formats. | [>100][GREEN]#,##0;[<=-100][YELLOW]#,##0;[BLUE]#,##0 |
| E | Scientific notation format. | #E+# – will display 1,500,500 as 2E+6 |
| [color] | Formats the text or number in the color specified | [Green]###.##[Red]-###.### |
Example
//Set the cell value as $125,571.35
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);New object("value";125571.35;"format";"_($* #,##0.00_)")Date and time formats
4D View Pro provides the following constants for ISO 8601 date and time patterns:
| Constant | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
vk pattern full date time |
“fullDateTimePattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the full date and time in current localization.USA default pattern: “dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss” |
vk pattern long date |
“longDatePattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the full date in current localization.USA default pattern: “dddd, dd MMMM yyyy” |
vk pattern long time |
“longTimePattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the time in current localization.USA default pattern: “HH:mm:ss” |
vk pattern month day |
“monthDayPattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the month and day in current localization.USA default pattern: “MMMM dd” |
vk pattern short date |
“shortDatePattern“ | Abbreviated ISO 8601 format for the date in current localization.USA default pattern: “MM/dd/yyyy” |
vk pattern short time |
“shortTimePattern“ | Abbreviated ISO 8601 format for the time in current localization.USA default pattern: “HH:mm” |
vk pattern sortable date time |
“sortableDateTimePattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the date and time in current localization which can be sorted.USA default pattern: “yyyy\’-\’MM\’-\’dd\’T\’HH\’:\’mm\’:\’ss” |
vk pattern universal sortable date time |
“universalSortableDateTimePattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the date and time in current localization using UTC which can be sorted.USA default pattern: “yyyy\’-\’MM\’-\’dd HH\’:\’mm\’:\’ss\’Z\'” |
vk pattern year month |
“yearMonthPattern“ | ISO 8601 format for the month and year in current localization.USA default pattern: “yyyy MMMM” |
Example
//Set the cell value as specific date and time
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;9);New object("value";!2024-12-18!);"time";?14:30:10?;"format";vk pattern full date time))Custom date and time formats
To create your own date and time patterns, in your current localization, you can use combinations of the following codes:
| Code (not case-sensitive) |
Description | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | (January 1, 2019) | ||
| m | Month number without leading zero | 1 | |
| mm | Month number with leading zero | 01 | |
| mmm | Month name, short | Jan | |
| mmmm | Month name, long | January | |
| d | Day number without leading zero | 1 | |
| dd | Day number with leading zero | 01 | |
| ddd | Day of week, short | Tue | |
| dddd | Day of week, long | Tuesday | |
| yy | Year, short | 19 | |
| yyyy | Year, long | 2019 | |
| Time | (2:03:05 PM) | ||
| h | Hour without leading zero. 0-23 | 2 | |
| hh | Hour with leading zero. 00-23 | 02 | |
| m | Minutes without leading zero. 0-59 | 3 | |
| mm | Minutes with leading zero. 00-59 | 03 | |
| s | Seconds without leading zero. 0-59 | 5 | |
| ss | Seconds with leading zero. 00-59 | 05 | |
| [h] | Elapsed time in hours | 14 (can exceed 24) | |
| [mm] | Elapsed time in minutes | 843 | |
| (ss] | Elapsed time in seconds | 50585 | |
| AM/PM | Periods of day. 24 hour fomat used if omitted. | PM |
The code ‘m’ is interpreted depending on its position in the pattern. If it’s immediately after ‘h’ or ‘hh’ or immediately before ‘s’ or ‘ss’, it will be interpreted as minutes, otherwise it will be interpreted as months.
Additional symbols
In addition to the special characters and codes described in the previous sections, there are additional characters and symbols that can be used in your format patterns. These additional characters and symbols do not require a \ or “” and do not impact the interpretation of the format pattern. They appear “as-is” within the pattern.
| Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + and – | Plus and minus signs | ### + ### = ###,### |
| ( ) | Left and right parenthesis | (-###.##) |
| : | Colon | hh:mm:ss |
| ^ | Caret | #\^# |
| ‘ | Apostrophe | ‘###### |
| { } | Curly brackets | {###,###,###} |
< > |
Less-than and greater than signs | ## >## |
| = | Equal sign | #+#=## |
| / | Forward slash. When used with numbers, displays them as fractions. | mm/dd/yyyy |
| ! | Exclamation point | $###.00! |
| & | Ampersand | “Hello” & “Welcome” |
| ~ | Tilde | ~## |
| Space character | ||
| € | Euro | €###.00 |
| £ | British Pound | £###.00 |
| ¥ | Japanese Yen | ¥###.00 |
| $ | Dollar sign | $###.00 |
| ¢ | Cent sign | .00¢ |
Print Attributes
4D View Pro print attributes allow you to control all aspects of printing 4D View Pro areas. These attributes are handled by the following commands:
Columns / Rows
Column and row attributes are used to specify the beginning, end, and repetition of columns and rows.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| columnEnd | longint | The last column to print in a cell range. Default value = -1 (all columns) |
| columnStart | longint | The first column to print in a cell range. Default value = -1 (all columns) |
| repeatColumnEnd | longint | The last column of a range of columns to print on the left of each page. Default value = -1 (all columns) |
| repeatColumnStart | longint | The first column of a range of columns to print on the left of each page. Default value = -1 (all columns) |
| repeatRowEnd | longint | The last row of a range of rows to print on the top of each page. Default value = -1 (all rows) |
| repeatRowStart | longint | The first row of a range of rows to print at the top of each page. Default value = -1 (all rows) |
| rowEnd | longint | The last row to print in a cell range. Default value = -1 (all rows) |
| rowStart | longint | The first row to print in a cell range. Default value = -1 (all rows) |
Headers / Footers
Header and footer attributes are used to specify text or images in the left, right, and center header/footer sections.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| footerCenter | text | The text and format of the center footer on printed pages. |
| footerCenterImage | picture | text* | The image for the center section of the footer. |
| footerLeft | text | The text and format of the left footer on printed pages. |
| footerLeftImage | picture | text* | The image for the left section of the footer. |
| footerRight | text | The text and format of the right footer on printed pages. |
| footerRightImage | picture | text* | The image for the right section of the footer. |
| headerCenter | text | The text and format of the center header on printed pages. |
| headerCenterImage | picture | text* | The image for the center section of the header. |
| headerLeft | text | The text and format of the left header on printed pages. |
| headerLeftImage | picture | text* | The image for the left section of the header. |
| headerRight | text | The text and format of the right header on printed pages. |
| headerRightImage | picture | text* | The image for the right section of the header. |
* If using text type, pass the filepath (absolute or relative) of the image. If you pass a relative path, the file should be located next to the database structure file. In Windows, the file extension must be indicated. No matter the type used to set an image, the image itself (not a reference) is stored in the 4D View Pro area and is returned by VP Get print info.
Special Characters
The following special characters allow the automatic addition or formatting of information in the header and footer when the 4D View Pro area is printed.
| Character | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| & | Escape character | (see examples below) | |
| P | Current page | printInfo.headerLeft:=”This is page &P.” | This is page 5. |
| N | Page count | printInfo.headerLeft:=”There are &N pages.” | There are 10 pages. |
| D | Current date (yyyy/mm/dd format) | printInfo.headerLeft:=”It is &D.” | It is 2015/6/19. |
| T | Current time | printInfo.headerLeft:=”It is &T.” | It is 16:30:36. |
| G | Image | printInfo.headerLeftImage:=smiley printInfo.headerLeft:=”&G” |
 |
| S | Strikethrough | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&SThis is text.” | |
| U | Underline | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&UThis is text.” | This is text. (Underlined) |
| B | Bold | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&BThis is text.” | This is text. |
| I | Italic | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&IThis is text.” | This is text. |
| “ | Font prefix | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&\”Lucida Console\”&14This is text.” | |
| K | Text Color prefix | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&KFF0000This is text.” | This is text (in red). |
| F | Workbook name | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&F” | 2019 Monthly Revenue Forecasts |
| A | Spreadsheet name | printInfo.headerLeft:=”&A” | June 2019 revenue forecast |
Margins
Margin attributes are used to specify the 4D View Pro area margins for printing. Expressed in hundreds of an inch.
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| margin | object | The print margins | |
| top | longint | Top margin, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 75 | |
| bottom | longint | Bottom margin, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 75 | |
| left | longint | Left margin, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 70 | |
| right | longint | Right margin, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 70 | |
| header | longint | Header offset, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 30 | |
| footer | longint | Footer offset, in hundredths of an inch. Default value = 30 |
Orientation
Orientation attributes are used to specify the direction the printed page layout.
This attribute defines rendering information only.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| orientation | longint | Page orientation. Available values: vk print page orientation landscape, vk print page orientation portrait(default) |
Page
Page attributes are used to specify general document print settings.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| blackAndWhite | boolean | Printing in black and white only. Default value = falseNote: PDFs are not affected by this attribute. Colors in PDFs remain. |
| centering | longint | How the contents are centered on the printed page. Available values: vk print centering both, vk print centering horizontal, vk print centering none (default), vk print centering vertical |
| firstPageNumber | longint | The page number to print on the first page.Default value = 1 |
| pageOrder | longint | The order pages are printed. Available values: vk print page order auto (default), vk print page order down then over, vk print page order over then down. |
| pageRange | text | The range of pages for printing |
| qualityFactor | longint | The quality factor for printing (1 – 8). The higher the quality factor, the better the printing quality, however printing performance may be affected.Default value = 2 |
| useMax | boolean | Only columns and rows with data are printed.Default value = true |
| zoomFactor | real | The amount to enlarge or reduce the printed page.Default value = 1 |
Paper Size
Paper size attributes are used to specify the dimensions or model of paper to use for printing. There are two ways to define paper size:
- Custom size – height and width attributes
- Standard size – kind attribute
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| paperSize | object | Paper dimensions (height, width) or specific format (kind) for printing. | |
| height | longint | Height of the paper, in hundredths of an inch. | |
| width | longint | Width of the paper, in hundredths of an inch. | |
| kind | text | Name of standard paper size (e.g., A2, A4, legal, etc.) returned by Get Print Option. Default value = “letter” |
- If the paper size is specified using the
heightandwidthproperties,VP Get print inforeturns a paper size withcustomas value forkind. - If you set the paper size using the
kindproperty, you can use either:- one of the formats in the SpreadJS format list
- one of the formats returned by the
PRINT OPTION VALUEScommand. In that case,VP Get print inforeturns the corresponding format with the height and width.
Scale
Scale attributes are used to specify printing optimization and adjustments.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bestFitColumns | boolean | Column width is adjusted to fit the largest text width for printing. Default value = “false” |
| bestFitRows | boolean | Row height is adjusted to fit the tallest text height for printing. Default value = “false” |
| fitPagesTall | longint | The number of vertical pages (portrait orientation) to check when optimizing printing. Default value = -1 |
| fitPagesWide | longint | The number of horizontal pages (landscape orientation) to check when optimizing printing. Default value = -1 |
Show / Hide
Show / Hide attributes are used to specify the visibility (printing) of 4D View Pro area elements.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| showBorder | boolean | Prints the outline border.Default value = “true” |
| showColumnHeader | longint | Column header print settings. Available values: vk print visibility hide, vk print visibility inherit (default), vk print visibility show, vk print visibility show once |
| showGridLine | boolean | Prints the gridlines. Default value = “false” |
| showRowHeader | longint | Row headers print settings. Available values: vk print visibility hide, vk print visibility inherit (default), vk print visibility show, vk print visibility show once |
Watermark
Watermark attributes are used to superimpose text or an image onto the 4D View Pro area.
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| watermark | collection | Collection of watermark settings. Default value: undefined | |
| [ ].height | longint | The height of the watermark text / image. | |
| [].imageSrc | picture |text* | The watermark text / image. | |
| [ ].page | text | The page(s) where the watermark is printed. For all pages: “all”. For specific pages: page numbers or page ranges separated by commas. Ex.: “1,3,5-12” | |
| [ ].width | longint | The width of the watermark text / image. | |
| [ ].x | longint | The horizontal coordinate of the top left point of the watermark text / image. | |
| [ ].y | longint | The vertical coordinate of the top left point of the watermark text / image. |
* If using text type, pass the filepath (absolute or relative) of the image. If you pass a relative path, the file should be located next to the database structure file. In Windows, the file extension must be indicated. No matter the type used to set an image, the image itself (not a reference) is stored in the 4D View Pro area and is returned by VP Get print info.
Style Objects
4D View Pro style objects and style sheets allow you to control the graphical aspects and the look of your 4D View Pro documents.
Style objects & Style sheets
Style objects contain the style settings. They can be used either in a style sheet or on their own. Style objects can also be used in addition to a style sheet so that different settings can be specified for individual cell ranges without affecting the rest of the document. You can use style objects directly with the VP SET CELL STYLE and VP SET DEFAULT STYLE commands. You can also use style objects when defining custom table themes using the VP SET TABLE THEME or VP CREATE TABLE commands.
A style sheet groups together a combination of properties in a style object to specify the look of all of the cells in your 4D View Pro documents. Style sheets saved with the document can be used to set the properties for a single sheet, multiple sheets, or an entire workbook. When created, a 4D View Pro style sheet is given a name which is saved within the style sheet in the “name” property. This allows a style sheet to be easily used and, if thoughtfully selected, can facilitate its identification and purpose (e.g., Letterhead_internal, Letterhead_external).
Style sheets are created with the VP ADD STYLESHEET command and applied with the the VP SET DEFAULT STYLE or VP SET CELL STYLEcommands. You can remove a style sheet with the VP REMOVE STYLESHEET command.
The VP Get stylesheet command can be used to return the style object of a single style sheet or you can use the VP Get stylesheets command to retrieve a collection of style objects for multiple style sheets.
Style object properties
Example:
$style:=New object
$style.hAlign:=vk horizontal align left
$style.font:="12pt papyrus"
$style.backColor:="#E6E6FA" //light purple color
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE("myDoc";$style)Background & Foreground
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| backColor | text | Defines the color of the background. | CSS color “#rrggbb” syntax (preferred syntax), CSS color “rgb(r,g,b)” syntax (alternate syntax), CSS color name (alternate syntax) |
| backgroundImage | picture, text | Specifies a background image. | Can be specified directly or via the image path (full path or file name only). If the file name only is used, the file must be located next to the database structure file. No matter how set (picture or text), a picture is saved with the document. This could impact the size of a document if the image is large. Note for Windows: File extension must be included. |
| backgroundImageLayout | longint | Defines the layout for the background image. | vk image layout center, vk image layout none, vk image layout stretch, vk image layout zoom |
| foreColor | text | Defines the color of the foreground. | CSS color “#rrggbb” syntax (preferred syntax), CSS color “rgb(r,g,b)” syntax (alternate syntax), CSS color name (alternate syntax) |
Borders
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| borderBottom, borderLeft, borderRight, borderTop, diagonalDown, diagonalUp | object | Defines the corresponding border line | ||
| color | text | Defines the color of the border. Default = black. | CSS color “#rrggbb” syntax (preferred syntax), CSS color “rgb(r,g,b)” syntax (alternate syntax), CSS color name (alternate syntax) | |
| style | longint | Defines the style of the border. Default = empty. Cannot be null or undefined. | vk line style dash dot, vk line style dash dot dot, vk line style dashed, vk line style dotted, vk line style double, vk line style empty, vk line style hair, vk line style medium, vk line style medium dash dot, vk line style medium dash dot dot,vk line style medium dashed, vk line style slanted dash dot, vk line style thick |
Fonts and text
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| font | text | Specifies the font characteristics in CSS font shorthand (“font-style font-variant font-weight font-size/line-height font-family”). Example: “14pt Century Gothic”. The font-size and font-family values are mandatory. If one of the other values is missing, their default values are used. Note: If a font name contains a space, the name must be within quotes. | A CSS font shorthand. 4D provides utility commands to handle font characteristics as objects: VP Font to object and VP Object to font |
|
| formatter | text | Pattern for value/time property. | Number/text/date/time formats, special characters. See Cell Format. | |
| isVerticalText | boolean | Specifies text direction. | True = vertical text, False = horizontal text. | |
| labelOptions | object | Defines cell label options (watermark options). | ||
| alignment | longint | Specifies the position of the cell label. Optional property. | vk label alignment top left, vk label alignment bottom left, vk label alignment top center, vk label alignment bottom center, vk label alignment top right, vk label alignment bottom right |
|
| visibility | longint | Specifies the visibility of the cell label. Optional property. | vk label visibility auto, vk label visibility hidden, vk label visibility visible |
|
| foreColor | text | Defines the color of the foreground. Optional property. | CSS color “#rrggbb” syntax (preferred syntax), CSS color “rgb(r,g,b)” syntax (alternate syntax), CSS color name (alternate syntax) | |
| font | text | Specifies the font characteristics with CSS font shorthand (“font-style font-variant font-weight font-size/line-height font-family”). The font-size and font-family values are mandatory. | ||
| textDecoration | longint | Specifies the decoration added to text. | vk text decoration double underline, vk text decoration line through, vk text decoration none, vk text decoration overline, vk text decoration underline |
|
| textIndent | longint | Defines the unit of text indention. 1 = 8 pixels | ||
| textOrientation | longint | Defines the rotation angle of the text in a cell. Number between -90 and 90 | ||
| watermark | text | Defines the watermark (cell label) content | ||
| wordWrap | boolean | Specifies if text should be wrapped. | True = wrapped text, False = unwrapped text |
Layout
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| cellPadding | text | Defines the cell padding | |
| hAlign | longint | Defines the horizontal alignment of cell contents. | vk horizontal align center, vk horizontal align general, vk horizontal align left, vk horizontal align right |
| locked | boolean | Specifies cell protection status. Note, this is only available if sheet protection is enabled. | True = locked, False = unlocked. |
| shrinkToFit | boolean | Specifies if the contents of the cell should be reduced. | True = reduced content, False = no reduction. |
| tabStop | boolean | Specifies if the focus to the cell can be set using the Tab key. | True = Tab key sets focus, False = Tab key does not set focus. |
| vAlign | longint | Specifies the vertical alignment of cell contents. | vk vertical align bottom, vk vertical align center, vk vertical align top |
Style information
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | text | Defines the name of the style |
| parentName | text | Specifies the style that the current style is based on. Values from the parent style will be applied, then any values from the current style are applied. Changes made in the current style will not be refelected in the parent style. Only available when using a style sheet. |
4D View Pro Object
The 4D View Pro object stores the whole spreadsheet contents. It is automatically handled by 4D View Pro. You can set or get this object using the VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT or VP Export to object methods.
It contains the following properties:
| Property | Value type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| version | Longint | Internal component version |
| dateCreation | Timestamp | Creation date |
| dateModified | Timestamp | Last modification date |
| meta | Object | Free contents, reserved for the 4D developer |
| spreadJS | Object | Reserved for the 4D View Pro component |
4D View Pro Form Object Variable
The 4D View Pro form object variable is the object variable associated to the 4D View Pro form area. It manages information used by the 4D View Pro object.
The 4D View Pro form object variable is for information purposes only (i.e., debugging). Under no circumstances should it be modified.
It contains the following properties:
| Property | Value type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ViewPro.area | Text | 4D View Pro area name |
| ViewPro.callbacks | Object | Stores temporary information necessary for commands requiring callbacks such as importing and exporting. |
| ViewPro.commandBuffers | Collection | Stores sequentially the commands called by the method and executes them as a batch (rather than individually) upon exiting the method, or if a command returns a value or the VP FLUSH COMMANDS is called. This mechanism increases performance by reducing the number of requests sent. |
| ViewPro.events | Object | Event list. |
| ViewPro.formulaBar | Boolean | Indicates whether or not the formula bar is displayed. Available only for the “toolbar” interface. |
| ViewPro.inited | Boolean | Indicates whether or not the 4D View Pro area has been initialized (see On VP Ready event). |
| ViewPro.interface | Text | Specifies the type of user interface:”ribbon”, “toolbar”, “none”. |
Formulas and Functions
Using formulas
A spreadsheet formula is an expression that calculates the value of a cell.
Entering formulas
To enter a formula in a 4D View Pro area:
- Select the cell into which you will enter the formula or function.
- Enter = (the equal sign).
- Type the formula and hit the Enter key.
When writing a formula, you can use different shortcuts:
- click on a cell to enter its reference in the formula:
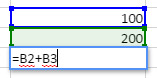
- type the first letter of a function to enter. A pop-up menu listing the available functions and references appears, allowing you to select the desired elements:
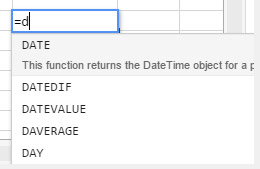
You can also create named formulas that can be called via their name. To do so, enter these formulas using the VP ADD FORMULA NAMEcommand.
Operators and Operands
All formulas have operands and operators:
- Operators: see Values and operators below.
- Operands include several categories:
- values (5 data types are supported)
- references to other cells (relative, absolute, mixed or by name)
- standard spreadsheet functions
- 4D functions based upon 4D formulas and providing access to 4D variables, fields, methods, commands, or expressions.
Values and operators
4D View Pro supports five types of data. For each data type, specific literal values and operators are supported.
| Data types | Values | Operators |
|---|---|---|
| Number | 1.2 1.2 E3 1.2E-3 10.3x |
+ (addition) – (subtraction) * (multiplication) / (division) ^ (exponent, the number of times to multiply a number by itself) % (percentage — divide the number before the operator by one hundred) |
| Date | 10/24/2017 | + (date + number of days -> date) + (date + time -> date + time of day) – (date – number of days -> date) – (date – date -> number of days between the two) |
| Time | 10:12:10 | Duration operators: + (addition) – (subtraction) (duration number -> duration) / (duration / number -> duration) |
| String | ‘Sophie’ or “Sophie” | & (concatenation) |
| Boolean | TRUE or FALSE | – |
Comparison operators
The following operators can be used with two operands of the same type:
| Operator | Comparison |
|---|---|
| = | equal to |
<> |
different than |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| <= | less than or equal to |
Operator precedence
List of operators from most to least important:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| () | Parenthesis (for grouping) |
| – | Negate |
| + | Plus |
| % | Percent |
| ^ | Exponent |
| * and / | Multiply and divide |
| + and – | Add and Subtract |
| & | Concatenate |
= > < >= <= <> |
Compare |
Cell references
Formulas often refer to other cells by cell addresses. You can copy these formulas into other cells. For example, the following formula, entered in cell C8, adds the values in the two cells above it and displays the result.
= C6 + C7This formula refers to cells C6 and C7. That is, 4D View Pro is instructed to refer to these other cells for values to use in the formula.
When you copy or move these formulas to new locations, each cell address in that formula will either change or stay the same, depending on how it is typed.
- A reference that changes is called a relative reference, and refers to a cell by how far left/right and up/down it is from the cell with the formula.
- A reference that always points to a particular cell is called an absolute reference.
- You can also create a mixed reference which always points to a fixed row or column.
Reference Notation
If you use only cell coordinates, for example, C5, 4D View Pro interprets the reference as relative. You may make the reference an absolute reference by putting a dollar sign in front of the letter and the number, as in $C$5.
You can mix absolute and relative references by inserting a dollar sign in front of the letter or the number alone, for example, $C5 or C$5. A mixed reference allows you to specify either the row or the column as absolute, while allowing the other portion of the address to refer relatively.
A convenient, fast and accurate way to specify an absolute reference is to name the cell and use that name in place of the cell address. A reference to a named cell is always absolute. You can create or modify named cells or named cell ranges using the VP ADD RANGE NAMEmethod.
The following table shows the effect of the different notations:
| Example | Type of reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C5 | Relative | Reference is to the relative location of cell C5, depending on the location of the cell in which the reference is first used |
| $C$5 | Absolute | Reference is absolute. Will always refer to cell C5 no matter where it is used. |
| $C5 | Mixed | Reference is always to column C, but the row reference is relative to the location of the cell in which the reference is first used. |
| C$5 | Mixed | Reference is always to row 5, but the column reference is relative to the location of the cell in which the reference is first used |
| Cell name | Absolute | Reference is absolute. Will always refer to the named cell or range no matter where the reference is used. |
Built-in functions
Spreadsheet functions are preset formulas used to calculate cell values. When you type the first letter of the function to enter, a pop-up menu listing the available functions and references appears, allowing you to select the desired elements:
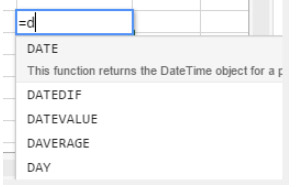
See SpreadJS’s extented list of functions for details and examples.
4D functions
4D View Pro allows you to define and call 4D custom functions, which execute 4D formulas. Using 4D custom functions extends the possibilities of your 4D View Pro documents and allows powerful interactions with the 4D database.
4D custom functions provide access, from within your 4D View Pro formulas, to:
- 4D process variables,
- fields,
- project methods,
- 4D language commands,
- or any valid 4D expression.
4D custom functions can receive parameters from the 4D View Pro area, and return values.
You declare all your functions using the VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSmethod. Examples:
o:=New object
//Name of the function in 4D View Pro: "DRIVERS_LICENCE"
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE:=New object
//process variable
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.formula:=Formula(DriverLicence)
//table field
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.formula:=Formula([Users]DriverLicence)
//project method
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.formula:=Formula(DriverLicenceState)
//4D command
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE:=Formula(Choose(DriverLicence; "Obtained"; "Failed"))
//4D expression and parameter
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.formula:=Formula(ds.Users.get($1).DriverLicence)
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.parameters:=New collection
$o.DRIVERS_LICENCE.parameters.push(New object("name"; "ID"; "type"; Is longint))See also 4D View Pro: Use 4D formulas in your spreadsheet (blog post)
Hello World example
We want to print “Hello World” in a 4D View Pro area cell using a 4D project method:
- Create a “myMethod” project method with the following code:
#DECLARE->$hw Text
$hw:="Hello World"
- Execute the following code before opening any form that contains a 4D View Pro area:
Case of
:(Form event code=On Load)
var $o : Object
$o:=New object
// Define "vpHello" function from the "myMethod" method
$o.vpHello:=New object
$o.vpHello.formula:=Formula(myMethod)
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS("ViewProArea";$o)
End case- Edit the content of a cell in a 4D View Pro area and type:
 “myMethod” is then called by 4D and the cell displays:
“myMethod” is then called by 4D and the cell displays: 
Parameters
Parameters can be passed to 4D functions that call project methods using the following syntax:
=METHODNAME(param1,param2,...,paramN)These parameters are received in methodName in $1, $2…$N.
Note that the ( ) are mandatory, even if no parameters are passed:
=METHODWITHOUTNAME()You can declare the name, type, and number of parameters through the parameters collection of the function you declared using the VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS method. Optionally, you can control the number of parameters passed by the user through minParams and maxParams properties.
For more information on supported incoming parameter types, please refer to the VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS method description.
If you do not declare parameters, values can be sequentially passed to methods (they will be received in $1, $2…) and their type will be automatically converted. Dates in jstype will be passed as object in 4D code with two properties:
|Property| Type| Description| |—|—|—| |value| Date| Date value| |time |Real| Time in seconds|
4D project methods can also return values in the 4D View Pro cell formula via $0. The following data types are supported for returned parameters:
- text (converted to string in 4D View Pro)
- real/longint (converted to number in 4D View Pro)
- date (converted to JS Date type in 4D View Pro – hour, minute, sec = 0)
- time (converted to JS Date type in 4D View Pro – date in base date, i.e. 12/30/1899)
- boolean (converted to bool in 4D View Pro)
- picture (jpg,png,gif,bmp,svg other types converted into png) creates a URI (data:image/png;base64,xxxx) and then used as the background in 4D View Pro in the cell where the formula is executed
- object with the following two properties (allowing passing a date and time):PropertyTypeDescriptionvalueDateDate valuetimeRealTime in seconds
If the 4D method returns nothing, an empty string is automatically returned.
An error is returned in the 4D View Pro cell if:
- the 4D method returns another type other than those listed above,
- an error occurred during 4D method execution (when user clicks on “abort” button).
Example
var $o : Object
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION:=New object
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.formula:=Formula(BirthInformation)
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.parameters:=New collection
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.parameters.push(New object("name";"First name";"type";Is text))
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.parameters.push(New object("name";"Birthday";"type";Is date))
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.parameters.push(New object("name";"Time of birth";"type";Is time))
$o.BIRTH_INFORMATION.summary:="Returns a formatted string from given information"
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS("ViewProArea"; $o)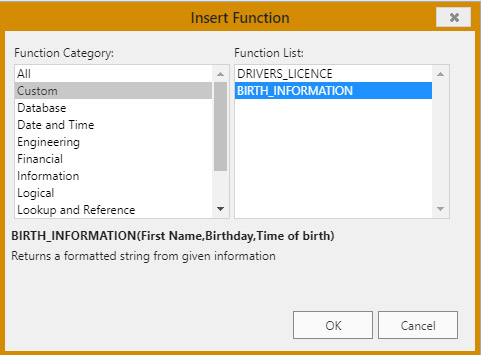
Compatibility
Alternate solutions are available to declare fields or methods as functions in your 4D View Pro areas. These solutions are maintained for compatibility reasons and can be used in specific cases. However, using the VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS method is recommended.
Referencing fields using the virtual structure
4D View Pro allows you to reference 4D fields using the virtual structure of the database, i.e. declared through the SET TABLE TITLES and/or SET FIELD TITLES commands with the * parameter. This alternate solution could be useful if your application already relies on a virtual structure (otherwise, using VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS is recommended).
WARNING: You cannot use the virtual structure and
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSsimultaneously. As soon asVP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSis called, the functions based uponSET TABLE TITLESandSET FIELD TITLEScommands are ignored in the 4D View Pro area.
Requirements
- The field must belong to the virtual structure of the database, i.e. it must be declared through the
SET TABLE TITLESand/orSET FIELD TITLEScommands with the * parameter (see example), - Table and field names must be ECMA compliant (see ECMA Script standard),
- The field type must be supported by 4D View Pro (see above).
An error is returned in the 4D View Pro cell if the formula calls a field which is not compliant.
Calling a virtual field in a formula
To insert a reference to a virtual field in a formula, enter the field with the following syntax:
TABLENAME_FIELDNAME()For example, if you declared the “Name” field of the “People” table in the virtual structure, you can call the following functions:
=PEOPLE_NAME()
=LEN(PEOPLE_NAME())If a field has the same name as a [4D method], it takes priority over the method.
Example
We want to print the name of a person in a 4D View Pro area cell using a 4D virtual field:
- Create an “Employee” table with a “L_Name” field:

- Execute the following code to initialize a virtual structure:
ARRAY TEXT($tableTitles;1)
ARRAY LONGINT($tableNum;1)
$tableTitles{1}:="Emp"
$tableNum{1}:=2
SET TABLE TITLES($tableTitles;$tableNum;*)ARRAY TEXT($fieldTitles;1)
ARRAY LONGINT($fieldNum;1)
$fieldTitles{1}:="Name"
$fieldNum{1}:=2 //last name
SET FIELD TITLES([Employee];$fieldTitles;$fieldNum;*) - Edit the content of a cell in the 4D View Pro area and enter “=e”:
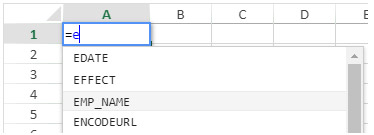
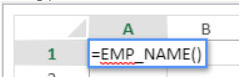
- Select EMP_NAME (use the Tab key) and enter the closing ).
- Validate the field to display the name of the current employee:
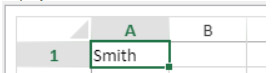
The [Employee] table must have a current record.
Declaring allowed methods
You can call directly 4D project methods from within your 4D View Pro formulas. For security reasons, you must declare explicitly methods that can be called by the user with the VP SET ALLOWED METHODSmethod.
Requirements
To be called in a 4D View Pro formula, a project method must be:
- Allowed: it was explicitly declared using the VP SET ALLOWED METHODS method.
- Runnable: it belongs to the host project or a loaded component with the “Shared by components and host project” option enabled (see Sharing of project methods).
- Not in conflict with an existing 4D View Pro spreadsheet function: if you call a project method with the same name as a 4D View Pro built-in function, the function is called.
If neither the VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS nor the VP SET ALLOWED METHODS method has been executed during the session, 4D View Pro custom functions rely on allowed methods defined by 4D’s generic
SET ALLOWED METHODScommand. In this case, the project method names must comply with JavaScript Identifier Grammar (see ECMA Script standard). The global filtering option in the Settings dialog box (see Data Access) is ignored in all cases.
Method List
Warning: The commands on this page are not thread-safe.
A – C – D – E – F – G – I – M – N – O – P – R – S
A
VP ADD FORMULA NAME
VP ADD FORMULA NAME ( vpAreaName : Text ; vpFormula : Text ; name : Text { ; options : Object } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| vpFormula | Text | -> | 4D View Pro formula |
| name | Text | -> | Name for the formula |
| options | Object | -> | Options for the named formula |
Description
The VP ADD FORMULA NAME command creates or modifies a named formula in the open document.
Named formulas created by this command are saved with the document.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the 4D View Pro formula that you want to name in vpFormula. For detailed information about formula syntax, see Formulas and Functions page.
Pass the new name for the formula in name. If the name is already used within the same scope, the new named formula replaces the existing one. Note that you can use the same name for different scopes (see below).
You can pass an object with additional properties for the named formula in options. The following properties are supported:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| scope | Number | Scope for the formula. You can pass the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or use the following constants: vk current sheetvk workbookThe scope determines whether a formula name is local to a given worksheet (scope=sheet index or vk current sheet), or global across the entire workbook (scope=vk workbook). |
| comment | Text | Comment associated to named formula |
Example
VP ADD FORMULA NAME("ViewProArea";"SUM($A$1:$A$10)";"Total2")See also
Cell references
VP ADD RANGE NAME
VP Get formula by name
VP Get names
VP ADD RANGE NAME
VP ADD RANGE NAME ( rangeObj : Object ; name : Text { ; options : Object } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| name | Text | -> | Name for the fomula |
| options | Object | -> | Options for the named formula |
Description
The VP ADD RANGE NAME command creates or modifies a named range in the open document.
Named ranges created by this command are saved with the document.
In rangeObj, pass the range that you want to name and in name, pass the new name for the range. If the name is already used within the same scope, the new named range replaces the existing one. Note that you can use the same name for different scopes (see below).
You can pass an object with additional properties for the named range in options. The following properties are supported:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| scope | Number | Scope for the range. You can pass the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or use the following constants: vk current sheetvk workbookThe scope determines whether a range name is local to a given worksheet (scope=sheet index or vk current sheet), or global across the entire workbook (scope=vk workbook). |
| comment | Text | Comment associated to named range |
- A named range is actually a named formula containing coordinates.
VP ADD RANGE NAMEfacilitates the creation of named ranges, but you can also use theVP ADD FORMULA NAMEmethod to create named ranges.- Formulas defining named ranges can be retrieved with the
VP Get formula by namemethod.
Example
You want to create a named range for a cell range:
$range:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";2;10)
VP ADD RANGE NAME($range;"Total1")See also
VP ADD FORMULA NAME
VP Get formula by name
VP Get names
VP Name
VP ADD SELECTION
VP ADD SELECTION ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Text | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP ADD SELECTION command adds the specified cells to the currently selected cells.
In rangeObj, pass a range object of cells to add to the current selection.
The active cell is not modified.
Example
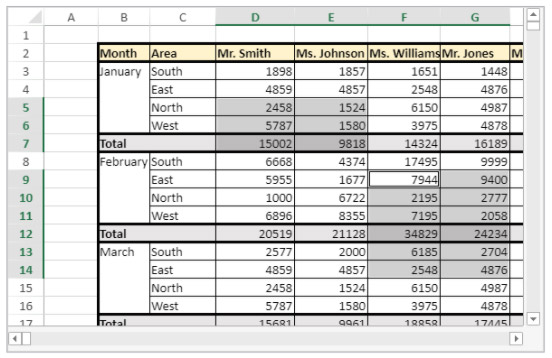
You have cells currently selected:
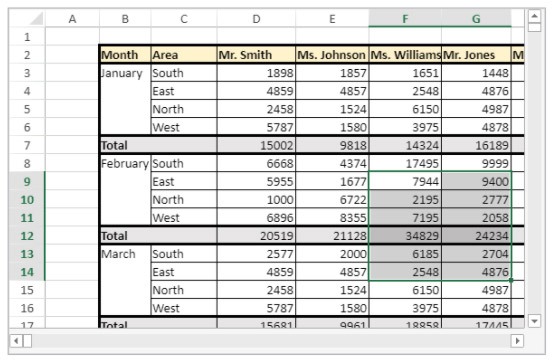
The following code will add cells to your selection:
$currentSelection:=VP Cells("myVPArea";3;4;2;3)
VP ADD SELECTION($currentSelection)Result:
See also
VP Get active cell
VP Get selection
VP RESET SELECTION
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP ADD SHEET
VP ADD SHEET ( vpAreaName : Text )
VP ADD SHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; index : Integer )
VP ADD SHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; sheet : Integer ; name : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Index of the new sheet |
| name | Text | -> | Sheet name |
Description
The VP ADD SHEET command inserts a sheet in the document loaded in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In sheet, you can pass an index for the new sheet. If the passed indexis inferior to or equal to 0, the command inserts the new sheet at the beginning. If index exceeds the number of sheets, the command inserts the new sheet after the existing ones.
Indexing starts at 0.
In name, you can pass a name for the new sheet. The new name cannot contain the following characters: *, :, [, ], ?,\,/
Example
The document currently has 3 sheets:

To insert a sheet at the third position (index 2) and name it “March”:
VP ADD SHEET("ViewProArea";2;"March")
See also
VP ADD SPAN
VP ADD SPAN ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP ADD SPAN command combines the cells in rangeObj as a single span of cells.
In rangeObj, pass a range object of cells. The cells in the range are joined to create a larger cell extending across multiple columns and/or rows. You can pass multiple cell ranges to create several spans at the same time. Note that if cell ranges overlap, only the first cell range is used.
- Only the data in the upper-left cell is displayed. Data in the other combined cells is hidden until the span is removed.
- Hidden data in spanned cells is accessible via formulas (beginning with the upper-left cell).
Example
To span the First quarter and Second quarter cells across the two cells beside them, and the South area cell across the two rows below it:
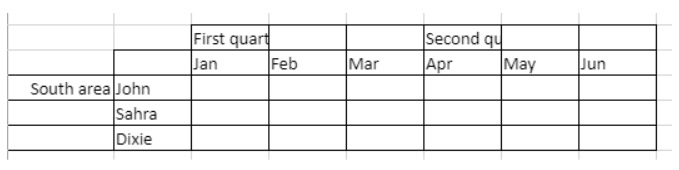
// First quarter range
$q1:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";2;3;3;1)
// Second quarter range
$q2:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";5;3;3;1)
// South area range
$south:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";0;5;1;3)
VP ADD SPAN(VP Combine ranges($q1;$q2;$south))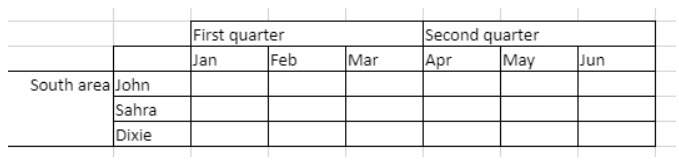
See also
4D View Pro Range Object Properties
VP Get spans
VP REMOVE SPAN
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP ADD STYLESHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; styleName : Text ; styleObj : Object { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| styleName | Text | -> | Name of style |
| styleObj | Object | -> | Object defining attribute settings |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP ADD STYLESHEET command creates or modifies the styleNamestyle sheet based upon the combination of the properties specified in styleObj in the open document. If a style sheet with the same name and index already exists in the document, this command will overwrite it with the new values.
Style sheets created by this command are saved with the document.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The styleName parameter lets you assign a name to the style sheet. If the name is already used within the same scope, the new style sheet replaces the existing one. Note that you can use the same name for different scopes (see below).
Within the styleObj, designate the settings for the style sheet (e.g., font, text decoration, alignment, borders, etc.). For the full list of style properties, see Style object properties.
You can designate where to define the style sheet in the optional sheetparameter using the sheet index (indexing starts at 0) or with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
If a styleName style sheet is defined at the workbook level and at a sheet level, the sheet level has priority over the workbook level when the style sheet is set.
To apply the style sheet, use the VP SET DEFAULT STYLE or VP SET CELL STYLE commands.
Example
The following code:
$styles:=New object
$styles.backColor:="green"
//Line Border Object
$borders:=New object("color";"green";"style";vk line style medium dash dot)
$styles.borderBottom:=$borders
$styles.borderLeft:=$borders
$styles.borderRight:=$borders
$styles.borderTop:=$borders
VP ADD STYLESHEET("ViewProArea";"GreenDashDotStyle";$styles)
//To apply the style
VP SET CELL STYLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea";1;1;2;2);New object("name";"GreenDashDotStyle"))will create and apply the following style object named GreenDashDotStyle:
{
backColor:green,
borderBottom:{color:green,style:10},
borderLeft:{color:green,style:10},
borderRight:{color:green,style:10},
borderTop:{color:green,style:10}
}See also
4D View Pro Style Objects and Style Sheets
VP Get stylesheet
VP Get stylesheets
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
VP All
VP All ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of all cells |
Description
The VP ALL command returns a new range object referencing all cells.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
You want to define a range object for all of the cells of the current spreadsheet:
$all:=VP All("ViewProArea") // all cells of the current sheetSee also
VP Cell
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP Row
C
VP Cell
VP Cell ( vpAreaName ; column : Integer ; row : Integer ; Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| column | Longint | -> | Column index |
| row | Longint | -> | Row index |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of a single cell |
Description
The VP Cell command returns a new range object referencing a specific cell.
This command is intended for ranges of a single cell. To create a range object for multiple cells, use the VP Cellscommand.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The column parameter defines the column of the cell range’s position. Pass the column index in this parameter.
The row parameter defines the row of the cell range’s position. Pass the row index in this parameter.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can indicate the index of the sheet where the range will be defined. If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used by default.
indexing starts at 0.
Example
You want to define a range object for the cell shown below (on the current spreadsheet):
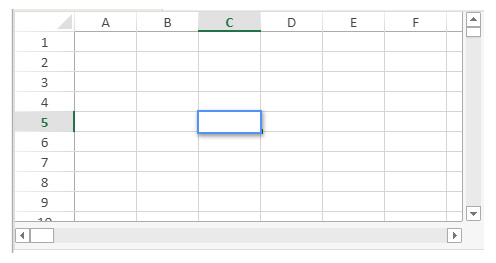
The code would be:
$cell:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";2;4) // C5See also
VP All
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP Row
VP Cells
VP Cells ( vpAreaName : Text ; column: Integer ; row: Integer ; columnCount : Integer ; rowCount : Integer { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v17 R4 | Added |
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| column | Integer | -> | Column index |
| row | Integer | -> | Row index |
| columnCount | Integer | -> | Number of columns |
| rowCount | Integer | -> | Number of rows |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of cells |
Description
The VP Cells command returns a new range object referencing specific cells.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The column parameter defines the first column of the cell range. Pass the column index (counting begins at 0) in this parameter. If the range is within multiple columns, you should also use the columnCount parameter.
In the row parameter, you can define the row(s) of the cell range’s position. Pass the row index (counting begins at 0) in this parameter. If the range is within multiple rows, you should also use the rowCount parameter.
The columnCount parameter allows you to define the total number of columns the range is within. columnCount must be greater than 0.
The rowCount parameter allows you to define the total number of rows the range is within. rowCount must be greater than 0.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used by default.
Example
You want to define a range object for the following cells (on the current sheet):

The code would be:
$cells:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";2;4;2;3) // C5 to D7See also
VP All
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP Row
VP Column
VP Column ( vpAreaName : Text ; column: Integer ; columnCount : Integer { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| column | Integer | -> | Column index |
| columnCount | Integer | -> | Number of columns |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of cells |
Description
The VP Column command returns a new range object referencing a specific column or columns.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The column parameter defines the first column of the column range. Pass the column index (counting begins at 0) in this parameter. If the range contains multiple columns, you should also use the optional columnCount parameter.
The optional columnCount parameter allows you to define the total number of columns of the range. columnCount must be greater than 0. If omitted, the value will be set to 1 by default and a column type range is created.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used by default.
Example
You want to define a range object for the column shown below (on the current spreadsheet):
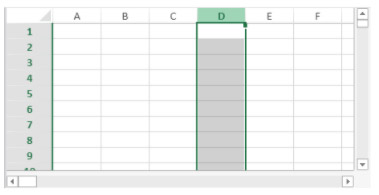
The code would be:
$column:=VP Column("ViewProArea";3) // column DSee also
VP All
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP Row
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP COLUMN AUTOFIT
VP COLUMN AUTOFIT ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP COLUMN AUTOFIT command automatically sizes the column(s) in rangeObj according to their contents.
In rangeObj, pass a range object containing a range of the columns whose size will be automatically handled.
Example
The following columns are all the same size and don’t display some of the text:
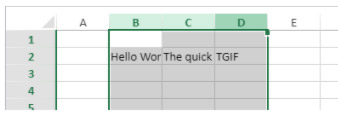
Selecting the columns and running this code:
VP COLUMN AUTOFIT(VP Get selection("ViewProarea"))… resizes the columns to fit the size of the contents:
See also
VP Combine ranges
VP Combine ranges ( rangeObj : Object ; otherRangeObj : Object {;…otherRangeObjN : Object } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| otherRangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Object | <- | Object containing a combined range |
Description
The VP Combine Ranges command returns a new range object that incorporates two or more existing range objects. All of the ranges must be from the same 4D View Pro area.
In rangeObj, pass the first range object.
In otherRangeObj, pass another range object(s) to combine with rangeObj.
The command incorporates rangeObj and otherRangeObjobjects by reference.
Example
You want to combine cell, column, and row range objects in a new, distinct range object:
$cell:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";2;4) // C5
$column:=VP Column("ViewProArea";3) // column D
$row:=VP Row("ViewProArea";9) // row 10
$combine:=VP Combine ranges($cell;$column;$row)See also
VP All
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP Row
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP Convert from 4D View
VP Convert from 4D View ( 4DViewDocument : Blob ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4DViewDocument | Blob | -> | 4D View document |
| Result | Object | <- | 4D View Pro object |
Description
The VP Convert from 4D View command allows you to convert a legacy 4D View document into a 4D View Pro object.
This command does not require that the legacy 4D View plug-in be installed in your environment.
In the 4DViewDocument parameter, pass a BLOB variable or field containing the 4D View document to convert. The command returns a 4D View Pro object into which all the information originally stored within the 4D View document is converted to 4D View Pro attributes.
Example
You want to get a 4D View Pro object from a 4D View area stored in a BLOB:
C_OBJECT($vpObj)
$vpObj:=VP Convert from 4D View($pvblob)VP Convert to picture
VP Convert to picture ( vpObject : Object {; rangeObj : Object} ) : Picture
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpObject | Object | -> | 4D View Pro object containing the area to convert |
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Object | <- | SVG picture of the area |
Description
The VP Convert to picture command converts the vpObject4D View Pro object (or the rangeObj range within vpObject) to a SVG picture.
This command is useful, for example:
- to embed a 4D View Pro document in an other document such as a 4D Write Pro document
- to print a 4D View Pro document without having to load it into a 4D View Pro area.
In vpObject, pass the 4D View Pro object that you want to convert. This object must have been previously parsed using VP Export to object or saved using VP EXPORT DOCUMENT.
SVG conversion process requires that expressions and formats (cf. Cell Format) included in the 4D View Pro area be evaluated at least once, so that they can be correctly exported. If you convert a document that was not evaluated beforehand, expressions or formats may be rendered in an unexpected way.
In rangeObj, pass a range of cells to convert. By default, if this parameter is omitted, the whole document contents are converted.
Document contents are converted with respect to their viewing attributes, including formats (see note above), visibility of headers, columns and rows. The conversion of the following elements is supported:
- Text : style / font / size / alignment / orientation / rotation / format
- Cell background : color / image
- Cell borders : thickness / color / style
- Cell merge
- Pictures
- Row height
- Column width
- Hidden columns / rows.
Gridline visibility depends on document attribute defined with VP SET PRINT INFO.
Function result
The command returns a picture in SVG format.
Example
You want to convert a 4D View Pro area in SVG, preview the result, and send it to a picture variable:
C_OBJECT($vpAreaObj)
C_PICTURE($vPict)
$vpAreaObj:=VP Export to object("ViewProArea")
$vPict:=VP Convert to picture($vpAreaObj) //export the whole areaSee also
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT
VP Export to object
VP SET PRINT INFO
VP Copy to object
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R4 | Added |
VP Copy to object ( rangeObj : Object {; options : Object} ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| options | Object | -> | Additional options |
| Result | Object | <- | Object returned. Contains the copied data |
Description
The VP Copy to object command copies the contents, style and formulas from rangeObj to an object.
In rangeObj, pass the cell range with the values, formatting, and formulas to copy. If rangeObj is a combined range, only the first one is used.
You can pass an optional options parameter with the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| copy | Boolean | True (default) to keep the copied values, formatting and formulas after the command executes. False to remove them. |
| copyOptions | Longint | Specifies what is copied or moved. Possible values: ValueDescriptionvk clipboard options all(default)Copies all data objects, including values, formatting, and formulas.vk clipboard options formattingCopies only the formatting.vk clipboard options formulasCopies only the formulas.vk clipboard options formulas and formattingCopies the formulas and formatting.vk clipboard options valuesCopies only the values.vk clipboard options value and formattingCopies the values and formatting. |
The paste options defined in the workbook options are taken into account.
The command returns an object that contains the copied data.
Example
This code sample first stores the contents, values, formatting and formulas from a range to an object, and then pastes them in another range:
var $originRange; $targetRange; $dataObject; $options : Object
$originRange:=VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 0; 0; 2; 5)
$options:=New object
$options.copy:=True
$options.copyOptions:=vk clipboard options all
$dataObject:=VP Copy to object($originRange; $options)
$targetRange:=VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 4; 0)
VP PASTE FROM OBJECT($targetRange; $dataObject; vk clipboard options all)See also
VP PASTE FROM OBJECT
VP MOVE CELLS
VP Get workbook options
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS
VP CREATE TABLE
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R8 | Support of theme options: bandColumns, bandRows, highlightFirstColumn, highlightLastColumn, theme |
| v19 R7 | Support of allowAutoExpand option |
| v19 R6 | Added |
VP CREATE TABLE ( rangeObj : Object ; tableName : Text {; source : Text} {; options : cs.ViewPro.TableOptions} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| tableName | Text | -> | Name for the table |
| source | Text | -> | Data context property name to display in the table |
| options | cs.ViewPro.TableOptions | -> | Additional options |
Description
The VP CREATE TABLE command creates a table in the specified range. You can create a table in a range of cells to make managing and analyzing a group of related data easier. A table typically contains related data in rows and columns, and takes advantage of a data context.
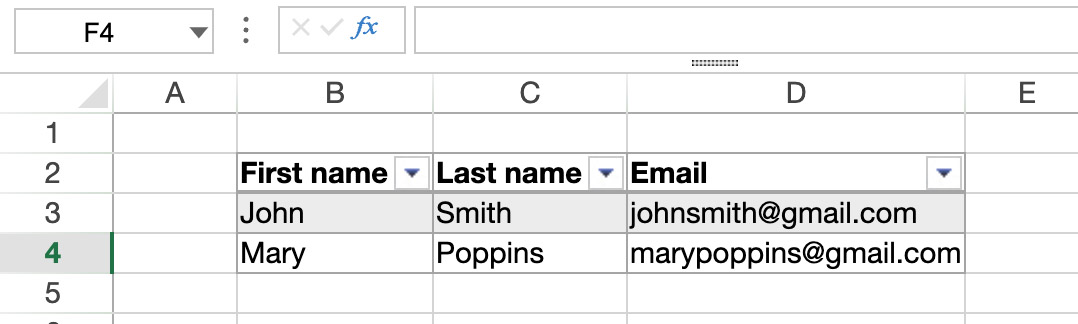
In rangeObj, pass the cell range where the table will be created.
In tableName, pass a name for the table. The name must:
- be unique in the sheet
- include at least 5 characters
- not include spaces or start with a number
In source, you can pass a property name of a data context to display its data in the table. This binds the table to the data context. When the data context is updated, the data displayed in the table is updated accordingly. The source property must contain a collection of objects and each element represents a row.
- If you don’t specify a source, the command creates an empty table with the size defined in rangeObj.
- If the specified source cannot be fully displayed in the document, no table is created.
In the options parameter, pass an object of the cs.ViewPro.TableOptions class that contains the table properties to set.
Within the options object, the tableColumns collection determines the structure of the table’s columns. The length of the tableColumns collection must be equal to the range column count:
- When the column count in rangeObj exceeds the number of columns in tableColumns, the table is filled with additional empty columns.
- When the column count in rangeObj is inferior to the number of tableColumns, the table displays a number of columns that match the range’s column count.
If you pass a source but no tableColumn option, the command generates columns automatically. In this case, rangeObj must be a cell range. Otherwise, the first cell of the range is used. When generating columns automatically, the following rules apply:
- If the data passed to the command is a collection of objects, the property names are used as column titles. For example:
([{ LastName: \"Freehafer\", FirstName: \"Nancy\"},{ LastName: \"John\", FirstName: \"Doe\"})Here the titles of the columns would be LastName and FirstName.
- If the data passed to the command is a collection of scalar values, it must contain a collection of subcollections:
- The first-level collection contains subcollections of values. Each subcollection defines a row. Pass an empty collection to skip a row. The number of values in the first subcollection determines how many columns are created.
- The subcollections’ indices are used as column titles.
- Each subcollection defines cell values for the row. Values can be
Integer,Real,Boolean,Text,Date,Null,TimeorPicture. ATimevalue must be an a object containing a time attribute, as described in VP SET VALUE.
This only works when generating columns automatically. You cannot use a collection of scalar data with the tableColumns option.
Example
To create a table using a data context:
// Set a data context
var $data : Object
$data:=New object()
$data.people:=New collection()
$data.people.push(New object("firstName"; "John"; "lastName"; "Smith"; "email"; "johnsmith@gmail.com"))
$data.people.push(New object("firstName"; "Mary"; "lastName"; "Poppins"; "email"; "marypoppins@gmail.com"))
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $data)
// Define the columns for the table
var $options : cs.ViewPro.TableOptions
$options:=cs.ViewPro.TableOptions.new()
$options.tableColumns:=New collection()
$options.tableColumns.push(cs.ViewPro.TableColumns.new("name"; "First name"; "dataField"; "firstName"))
$options.tableColumns.push(cs.ViewPro.TableColumns.new("name"; "Last name"; "dataField"; "lastName"))
$options.tableColumns.push(cs.ViewPro.TableColumns.new("name"; "Email"; "dataField"; "email"))
// Create a table from the "people" collection
VP CREATE TABLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 1; 1; $options.tableColumns.length; 1); "ContextTable"; "people"; $options)Here’s the result:

See also
VP Find table
VP Get table column attributes
VP Get table column index
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS
VP REMOVE TABLE
VP RESIZE TABLE
VP SET DATA CONTEXT
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP SET TABLE THEME
D
VP DELETE COLUMNS
VP DELETE COLUMNS ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP DELETE COLUMNS command removes the columns in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of columns to remove. If the passed range contains:
- both columns and rows, only the columns are removed.
- only rows, the command does nothing.
Columns are deleted from right to left.
Example
To delete columns selected by the user (in the image below columns B, C, and D):

use the following code:
VP DELETE COLUMNS(VP Get selection("ViewProArea"))See also
VP DELETE ROWS
VP DELETE ROWS ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP DELETE ROWS command removes the rows in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of rows to remove. If the passed range contains:
- both columns and rows, only the rows are removed.
- only columns, the command does nothing.
Rows are deleted from bottom to top.
Example
To delete rows selected by the user (in the image below rows 1, 2, and 3):

use the following code:
VP DELETE ROWS(VP Get selection("ViewProArea"))See also
E
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT ( vpAreaName : Text ; filePath : Text {; paramObj : Object} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| filePath | Text | -> | Pathname of the document |
| paramObj | Object | -> | Export options |
Description
The VP EXPORT DOCUMENT command exports the 4D View Pro object attached to the 4D View Pro area vpAreaName to a document on disk according to the filePath and paramObjparameters.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In filePath, pass the destination path and name of the document to be exported. If you don’t specify a path, the document will be saved at the same level as the Project folder.
You can specify the exported file’s format by including an extension after the document’s name:
- 4D View Pro (“.4vp”)
- Microsoft Excel (“.xlsx”)
- PDF (“.pdf”)
- CSV (“.txt”, or “.csv”)
If the extension is not included, but the format is specified in paramObj, the exported file will have the extension that corresponds to the format, except for the CSV format (no extension is added in this case).
The optional paramObj parameter allows you to define multiple properties for the exported 4D View Pro object, as well as launch a callback method when the export has completed.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| format | text | (optional) When present, designates the exported file format: “.4vp” (default), “.csv”, “.xlsx”, or “.pdf”. You can use the following constants:vk 4D View Pro formatvk csv formatvk MS Excel formatvk pdf format4D adds the appropriate extension to the file name if needed. If the format specified doesn’t correspond with the extension in filePath, it will be added to the end of filePath. If a format is not specified and no extension is provided in filePath, the default file format is used. |
| password | text | Microsoft Excel only (optional) – Password used to protect the MS Excel document |
| formula | object | Callback method to be launched when the export has completed. Using a callback method is necessary when the export is asynchronous (which is the case for PDF and Excel formats) if you need some code to be executed after the export. The callback method must be used with the Formulacommand (see below for more information). |
| valuesOnly | boolean | Specifies that only the values from formulas (if any) will be exported. |
| includeFormatInfo | boolean | True to include formatting information, false otherwise (default is true). Formatting information is useful in some cases, e.g. for export to SVG. On the other hand, setting this property to false allows reducing export time. |
| includeBindingSource | Boolean | 4DVP and Microsoft Excel only. True (default) to export the current data context values as cell values in the exported document (data contexts themselves are not exported). False otherwise. Cell binding is always exported. For data context and cell binding management, see VP SET DATA CONTEXTand VP SET BINDING PATH. |
| sheet | number | PDF only (optional) – Index of sheet to export (starting from 0). -2=all visible sheets (default), -1=current sheet only |
| pdfOptions | object | PDF only (optional) – Options for pdf export PropertyTypeDescriptioncreatortextname of the application that created the original document from which it was converted.titletexttitle of the document.authortextname of the person who created that document.keywordstextkeywords associated with the document.subjecttextsubject of the document. |
| csvOptions | object | CSV only (optional) – Options for csv export PropertyTypeDescriptionrangeobjectRange object of cellsrowDelimitertextRow delimiter. Default: “\r\n”columnDelimitertextColumn delimiter. Default: “,” |
\<customProperty> |
any | Any custom property that will be available through the $3 parameter in the callback method. |
Notes about Excel format:
- When exporting a 4D View Pro document into a Microsoft Excel-formatted file, some settings may be lost. For example, 4D methods and formulas are not supported by Excel. You can verify other settings with this list from GrapeCity.
- Exporting in this format is run asynchronously, use the formula property of the paramObj for code to be executed after the export.
Notes about PDF format:
- When exporting a 4D View Pro document in PDF, the fonts used in the document are automatically embedded in the PDF file. Only OpenType fonts (.OTF or .TTF files) having a Unicode map can be embedded. If no valid font file is found for a font, a default font is used instead.
- Exporting in this format is run asynchronously, use the formula property of the paramObj for code to be executed after the export.
Notes about CSV format:
- When exporting a 4D View Pro document to CSV, some settings may be lost, as only the text and values are saved.
- All the values are saved as double-quoted strings. For more information on delimiter-separated values, see this article on Wikipedia.
Once the export operation is finished, VP EXPORT DOCUMENTautomatically triggers the execution of the method set in the formula property of the paramObj, if used.
Passing a callback method (formula)
When including the optional paramObj parameter, the VP EXPORT DOCUMENT command allows you to use the Formulacommand to call a 4D method which will be executed once the export has completed. The callback method will receive the following values in local variables:
| Variable | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $1 | text | The name of the 4D View Pro object | |
| $2 | text | The filepath of the exported 4D View Pro object | |
| $3 | object | A reference to the command’s paramObj | |
| $4 | object | An object returned by the method with a status message | |
| .success | boolean | True if export with success, False otherwise. | |
| .errorCode | integer | Error code. May be returned by 4D or JavaScript. | |
| .errorMessage | text | Error message. May be returned by 4D or JavaScript. |
Example 1
You want to export the contents of the “VPArea” area to a 4D View Pro document on disk:
var $docPath: Text
$docPath:="C:\\Bases\\ViewProDocs\\MyExport.4VP"
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT("VPArea";$docPath)
//MyExport.4VP is saved on your diskExample 2
You want to export the current sheet in PDF:
var $params: Object
$params:=New object
$params.format:=vk pdf format
$params.sheet:=-1
$params.pdfOptions:=New object("title";"Annual Report";"author";Current user)
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT("VPArea";"report.pdf";$params)Example 3
You want to export a 4D View Pro document in “.xlsx” format and call a method that will launch Microsoft Excel with the document open once the export has completed:
$params:=New object
$params.formula:=Formula(AfterExport)
$params.format:=vp MS Excel format //".xlsx"
$params.valuesOnly:=True
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT("ViewProArea";"c:\\tmp\\convertedfile";$params)AfterExport method:
C_TEXT($1;$2)
C_OBJECT($3;$4)
$areaName:=$1
$filePath:=$2
$params:=$3
$status:=$4
If($status.success=False)
ALERT($status.errorMessage)
Else
LAUNCH EXTERNAL PROCESS("C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office15\\excel "+$filePath)
End ifExample 4
You want to export the current sheet to a .txt file with pipe-separated values:
var $params : Object
$params:=New object
$params.range:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";0;0;2;5)
$params.rowDelimiter:="\n"
$params.columnDelimiter:="|"
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT("ViewProArea";"c:\\tmp\\data.txt";New object("format";vk csv format;"csvOptions";$params))Here’s the result:

See also
VP Convert to picture
VP Export to object
VP Column
VP Print
VP Export to object
VP Export to object ( vpAreaName : Text {; options : Object} ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| options | Object | -> | Export options |
| Result | Object | <- | 4D View Pro object |
Description
The VP Export to object command returns the 4D View Pro object attached to the 4D View Pro area vpAreaName. You can use this command for example to store the 4D View Pro area in a 4D database object field.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the options parameter, you can pass the following export options, if required:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| includeFormatInfo | Boolean | True (default) to include formatting information, false otherwise. Formatting information is useful in some cases, e.g. for export to SVG. On the other hand, setting this property to False allows reducing export time. |
| includeBindingSource | Boolean | True (default) to export the current data context values as cell values in the exported object (data contexts themselves are not exported). False otherwise. Cell binding is always exported. |
For more information on 4D View Pro objects, please refer to the 4D View Pro object paragraph.
Example 1
You want to get the “version” property of the current 4D View Pro area:
var $vpAreaObj : Object
var $vpVersion : Number
$vpAreaObj:=VP Export to object("vpArea")
// $vpVersion:=OB Get($vpAreaObj;"version")
$vpVersion:=$vpAreaObj.versionExample 2
You want to export the area, excluding formatting information:
var $vpObj : Object
$vpObj:=VP Export to object("vpArea";New object("includeFormatInfo";False))See also
VP Convert to picture
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT
VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT
F
VP Find
VP Find ( rangeObj : Object ; searchValue : Text ) : Object
VP Find ( rangeObj : Object ; searchValue : Text ; searchCondition : Object } ) : Object
VP Find ( rangeObj : Object ; searchValue : Text ; searchCondition : Object ; replaceValue : Text ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| searchValue | Text | -> | Search value |
| searchCondition | Object | -> | Object containing search condition(s) |
| replaceValue | Text | -> | Replacement value |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object |
Description
The VP Find command searches the rangeObj for the searchValue. Optional parameters can be used to refine the search and/or replace any results found.
In the rangeObj parameter, pass an object containing a range to search.
The searchValue parameter lets you pass the text to search for within the rangeObj.
You can pass the optional searchCondition parameter to specify how the search is performed. The following properties are supported:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| afterColumn | Integer | The number of the column just before the starting column of the search. If the rangeObj is a combined range, the column number given must be from the first range. Default value: -1 (beginning of the rangeObj) |
| afterRow | Integer | The number of the row just before the starting row of the search. If the rangeObj is a combined range, the row number given must be from the first range. Default value: -1 (beginning of the rangeObj) |
| all | Boolean | True – All cells in rangeObjcorresponding to searchValueare returnedFalse – (default value) Only the first cell in rangeObjcorresponding to searchValue is returned |
| flags | Integer | vk find flag exact matchThe entire content of the cell must completely match the search valuevk find flag ignore caseCapital and lower-case letters are considered the same. Ex: “a” is the same as “A”.vk find flag noneno search flags are considered (default)vk find flag use wild cardsWildcard characters (*,?) can be used in the search string. Wildcard characters can be used in any string comparison to match any number of characters:* for zero or multiple characters (for example, searching for “bl*” can find “bl”, “black”, or “blob”)? for a single character (for example, searching for “h?t” can find “hot”, or “hit”These flags can be combined. For example: $search.flags:=vk find flag use wild cards+vk find flag ignore case |
| order | Integer | vk find order by columnsThe search is performed by columns. Each row of a column is searched before the search continues to the next column.vk find order by rowsThe search is performed by rows. Each column of a row is searched before the search continues to the next row (default) |
| target | Integer | vk find target formulaThe search is performed in the cell formulavk find target tagThe search is performed in the cell tagvk find target textThe search is performed in the cell text (default)These flags can be combined. For example:$search.target:=vk find target formula+vk find target text |
In the optional replaceValue parameter, you can pass text to take the place of any instance of the text in searchValue found in the rangeObj.
Returned Object
The function returns a range object describing each search value that was found or replaced. An empty range object is returned if no results are found.
Example 1
To find the first cell containing the word “Total”:
var $range;$result : Object
$range:=VP All("ViewProArea")
$result:=VP Find($range;"Total")Example 2
To find “Total” and replace it with “Grand Total”:
var $range;$condition;$result : Object
$range:=VP All("ViewProArea")
$condition:=New object
$condition.target:=vk find target text
$condition.all:=True //Search entire document
$condition.flags:=vk find flag exact match
// Replace the cells containing only 'Total' in the current sheet with "Grand Total"
$result:=VP Find($range;"Total";$condition;"Grand Total")
// Check for empty range object
If($result.ranges.length=0)
ALERT("No result found")
Else
ALERT($result.ranges.length+" results found")
End ifVP Find table
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP Find table ( rangeObj : Object ) : Text
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Cell range |
| Result | Text | <- | Table name |
Description
The VP Find table command returns the name of the table to which to the rangeObj cell belongs.
In rangeObj, pass a cell range object. If the designated cells do not belong to a table, the command returns an empty string.
If rangeObj is not a cell range or contains multiple ranges, the first cell of the first range is used.
Example
If (FORM Event.code=On After Edit && FORM Event.action="valueChanged")
$tableName:=VP Find table(FORM Event.range)
If ($tableName#"")
ALERT("The "+$tableName+" table has been modified.")
End if
End ifSee also
VP FLUSH COMMANDS
VP FLUSH COMMANDS ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
Description
The VP FLUSH COMMANDS command immediately executes stored commands and clears the command buffer.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In order to increase performance and reduce the number of requests sent, the 4D View Pro commands called by the developer are stored in a command buffer. When called, VP FLUSH COMMANDS executes the commands as a batch when leaving the method and empties the contents of the command buffer.
Example
You want to trace the execution of the commands and empty the command buffer:
VP SET TEXT VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea1";10;1);"INVOICE")
VP SET TEXT VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea1";10;2);"Invoice date: ")
VP SET TEXT VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea1";10;3);"Due date: ")
VP FLUSH COMMANDS(("ViewProArea1")
TRACEVP Font to object
VP Font to object ( font : Text ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| font | Text | -> | Font shorthand string |
| Result | Object | <- | Font object |
Description
The VP Font to object utility command returns an object from a font shorthand string. This object can then be used to set or get font property settings via object notation.
In the font parameter, pass a font shorthand string to specify the different properties of a font (e.g., “12 pt Arial”). You can learn more about font shorthand strings in this page for example.
The returned object contains defined font attributes as properties. For more information about the available properties, see the VP Object to font command.
Example 1
This code:
$font:=VP Font to object("16pt arial")will return the following $font object:
{
family:arial
size:16pt
}Example 2
See example for VP Object to font.
See also
4D View Pro Style Objects and Style Sheets
VP Object to font
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
G
VP Get active cell
VP Get active cell ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of single cell |
Description
The VP Get active cell command returns a new range object referencing the cell which has the focus and where new data will be entered (the active cell).
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
The following code will retrieve the coordinates of the active cell:
$activeCell:=VP Get active cell("myVPArea")
//returns a range object containing:
//$activeCell.ranges[0].column=3
//$activeCell.ranges[0].row=4
//$activeCell.ranges[0].sheet=0See also
VP ADD SELECTION
VP Get selection
VP RESET SELECTION
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP Get binding path
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R5 | Added |
VP Get binding path ( rangeObj : Object ) : Text
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Text | <- | Name of the attribute bound to the cell |
Description
The VP Get binding path command returns the name of the attribute bound to the cell specified in rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object that is either a cell range or a combined range of cells. Note that:
- If rangeObj is a range with several cells, the command returns the attribute name linked to the first cell in the range.
- If rangeObj contains several ranges of cells, the command returns the attribute name linked to the first cell of the first range.
Example
var $p; $options : Object
var $myAttribute : Text
$p:=New object
$p.firstName:="Freehafer"
$p.lastName:="Nancy"
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $p)
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 0; 0); "firstName")
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 1; 0); "lastName")
$myAttribute:=VP Get binding path(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 1; 0)) // "lastName"See also
VP SET BINDING PATH
VP Get data context
VP SET DATA CONTEXT
VP Get cell style
VP Get cell style ( rangeObj : Object ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Object | <- | Style object |
Description
The VP Get cell style command returns a style object for the first cell in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range containing the style to retrieve.
- If rangeObj contains a cell range, the cell style is returned.
- If rangeObj contains a range that is not a cell range, the style of the first cell in the range is returned.
- If rangeObj contains several ranges, only the style of the first cell in the first range is returned.
Example
To get the details about the style in the selected cell (B2):
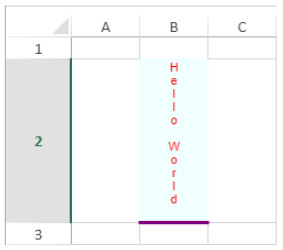
This code:
$cellStyle:=VP Get cell style(VP Get selection("myDoc"))… will return this object:
{
"backColor":"Azure",
"borderBottom":
{
"color":#800080,
"style":5
}
"font":"8pt Arial",
"foreColor":"red",
"hAlign":1,
"isVerticalText":"true",
"vAlign":0
}See also
VP GET DEFAULT STYLE
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP Get column attributes
VP Get column attributes ( rangeObj : Object ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of column properties |
Description
The VP Get column attributes command returns a collection of properties for any column in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of the columns whose attributes will be retrieved.
The returned collection contains any properties for the columns, whether or not they have been set by the VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES command.
Example
The following code:
C_OBJECT($range)
C_COLLECTION($attr)
$range:=VP Column("ViewProArea";1;2)
$attr:=VP Get column attributes($range)… will return a collection of the attributes within the given range:

See also
VP Get row attributes
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES
VP Get column count
VP Get column count ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area from object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Integer | <- | Total number of columns |
Description
The VP Get column count command returns the total number of columns from the designated sheet.
In vpAreaName, pass the name property of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can define where to get the column count in the optional sheet parameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
The following code returns the number of columns in the 4D View Pro area:
C_Integer($colCount)
$colCount:=VP Get column count("ViewProarea")See also
VP Get row count
VP SET COLUMN COUNT
VP SET ROW COUNT
VP Get current sheet
VP Get current sheet ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| Function result | Integer | <- | Index of the current sheet |
Description
The VP Get current sheet command returns the index of the current sheet in vpAreaName. The current sheet is the selected sheet in the document.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
When the third sheet is selected:

The command returns 2:
$index:=VP Get current sheet("ViewProArea")See also
VP Get data context
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R5 | Added |
VP Get data context ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
VP Get data context ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Object | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Index of the sheet to get the data context from |
| Result | Object |Collection | <- | Data context |
Description
The VP Get data context command returns the current data context of a worksheet. The returned context includes any modifications made to the contents of the data context.
In sheet, pass the index of the sheet to get the data context from. If no index is passed, the command returns the data context of the current worksheet. If there is no context for the worksheet, the command returns Null.
The function returns an object or a collection depending on the type of data context set with VP SET DATA CONTEXT.
Example
To get the data context bound to the following cells:

var $dataContext : Object
$dataContext:=VP Get data context("ViewProArea") // {firstName:Freehafer,lastName:Nancy}See also
VP SET DATA CONTEXT
VP Get binding path
VP SET BINDING PATH
VP Get default style
VP Get default style ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area from object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Integer | <- | Total number of columns |
Description
The VP Get default style command returns a default style object for a sheet. The returned object contains basic document rendering properties as well as the default style settings (if any) previously set by the VP SET DEFAULT STYLE method. For more information about style properties, see Style Objects & Style Sheets.
In vpAreaName, pass the name property of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can define where to get the column count in the optional sheet parameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
To get the details about the default style for this document:
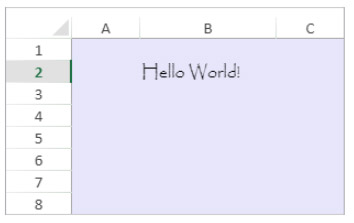
This code:
$defaultStyle:=VP Get default style("myDoc")will return this information in the $defaultStyle object:
{
backColor:#E6E6FA,
hAlign:0,
vAlign:0,
font:12pt papyrus
}See also
VP Get cell style
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
VP Get formula
VP Get formula ( rangeObj : Object) : Text
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Text | <- | Formula |
Description
The VP Get formula command retrieves the formula from a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range whose formula you want to retrieve. If rangeObj designates multiple cells or multiple ranges, the formula of the first cell is returned. If rangeObj is a cell that does not contain a formula, the method returns an empty string.
Example
//set a formula
VP SET FORMULA(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);"SUM($A$1:$C$10)")
$result:=VP Get formula(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2)) // $result="SUM($A$1:$C$10)"See also
VP Get formulas
VP SET FORMULA
VP SET ROW COUNT
VP Get formula by name
VP Get formula by name ( vpAreaName : Text ; name : Text { ; scope : Number } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| name | Text | -> | Name of the named range |
| scope | Number | -> | Target scope (default=current sheet) |
| Result | Text | <- | Named formula or named range definition |
Description
The VP Get formula by name command returns the formula and comment corresponding to the named range or named formula passed in the name parameter, or null if it does not exist in the defined scope.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the named range or named formula that you want to get in name. Note that named ranges are returned as formulas containing absolute cell references.
You can define where to get the formula in scope using either the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Returned Object
The returned object contains the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| formula | Text | Text of the formula corresponding to the named formula or named range. For named ranges, the formula is a sequence of absolute coordinates. |
| comment | Text | Comment corresponding to the named formula or named range |
Example
$range:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";0;0)
VP ADD RANGE NAME("Total1";$range)
$formula:=VP Get formula by name("ViewProArea";"Total1")
//$formula.formula=Sheet1!$A$1
$formula:=VP Get formula by name("ViewProArea";"Total")
//$formula=null (if not existing)See also
VP ADD FORMULA NAME
VP ADD RANGE NAME
VP Get names
VP Get formulas
VP Get formulas ( rangeObj : Object ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of formula values |
Description
The VP Get formulas command retrieves the formulas from a designated rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range whose formulas you want to retrieve. If rangeObj designates multiple ranges, the formula of the first range is returned. If rangeObj does not contain any formulas, the command returns an empty string.
The returned collection is two-dimensional:
- The first-level collection contains subcollections of formulas. Each subcollection reprensents a row.
- Each subcollection defines cell values for the row. Values are text elements containing the cell formulas.
Example
You want to retrieve the formulas in the Sum and Average columns from this document:
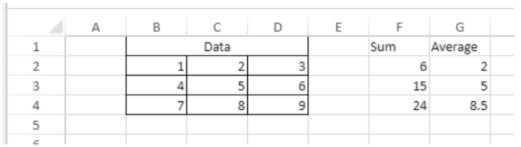
You can use this code:
$formulas:=VP Get formulas(VP Cells("ViewProArea";5;1;2;3))
//$formulas[0]=[Sum(B2:D2),Average(B2:D2)]
//$formulas[1]=[Sum(B3:D3),Average(B3:D3)]
//$formulas[2]=[Sum(B4:D4),Average(C4:D4)]See also
VP Get formula
VP Get values
VP SET FORMULAS
VP SET VALUES
VP Get frozen panes
VP Get frozen panes ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Object containing frozen column and row information |
Description
The VP Get frozen panes command returns an object with information about the frozen columns and rows in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Returned object
The command returns an object describing the frozen columns and rows. This object can contain the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| columnCount | Integer | The number of frozen columns on the left of the sheet |
| trailingColumnCount | Integer | The number of frozen columns on the right of the sheet |
| rowCount | Integer | The number of frozen rows on the top of the sheet |
| trailingRowCount | Integer | The number of frozen rows on the bottom of the sheet |
Example
You want to retrieve information about the number of frozen columns and rows:
var $panesObj : Object
$panesObj:=VP Get frozen panes("ViewProArea")The returned object contains, for example:
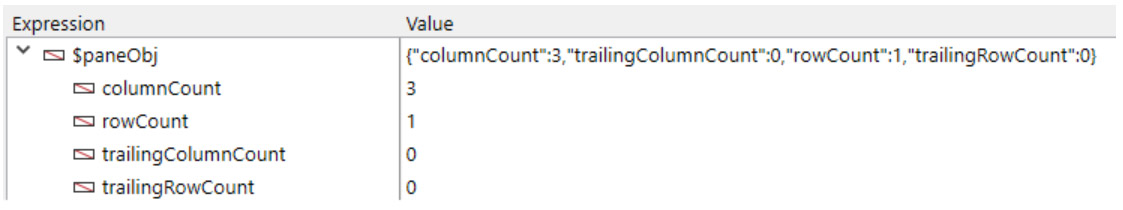
See also
VP Get names
VP Get names ( vpAreaName : Text { ; scope : Number } ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| scope | Number | -> | Target scope (default= current sheet) |
| Result | Collection | <- | Existing names in the defined scope |
Description
The VP Get names command returns a collection of all defined “names” in the current sheet or in the scope designated by the scope parameter.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can define where to get the names in scope using either the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Returned collection
The returned collection contains one object per name. The following object properties can be returned:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| result[ ].name | Text | cell or range name |
| result[ ].formula | Text | formula |
| result[].comment | Text | Comment associated to the name |
Available properties depend on the type of the named element (named cell, named range, or named formula).
Example
var $list : Collection
$list:=VP Get names("ViewProArea";2) //names in 3rd sheetSee also
VP ADD FORMULA NAME
VP ADD RANGE NAME
VP Get formula by name
VP Name
VP Get print info
VP Get print info ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Object of printing information |
Description
The VP Get print info command returns an object containing the print attributes of the vpAreaName.
Pass the the name of the 4D View Pro area in vpAreaName. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet (counting begins at 0) whose printing attributes you want returned. If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
This code:
$pinfo:=VP Get print info("ViewProArea")… returns the print attributes of the 4D View Pro area set in the VP SET PRINT INFO command:
{
bestFitColumns:false,
bestFitRows:false,
blackAndWhite:false,
centering:0,
columnEnd:8,
columnStart:0,
firstPageNumber:1,
fitPagesTall:1,
fitPagesWide:1,
footerCenter:"&BS.H.I.E.L.D. &A Sales Per Region",
footerCenterImage:,
footerLeft:,
footerLeftImage:,
footerRight:"page &P of &N",
footerRightImage:,
headerCenter:,
headerCenterImage:,
headerLeft:"&G",
headerLeftImage:logo.jpg,
headerRight:,
headerRightImage:,
margin:{top:75,bottom:75,left:70,right:70,header:30,footer:30},
orientation:2,
pageOrder:0,
pageRange:,
paperSize:{width:850,height:1100,kind:1},
qualityFactor:2,
repeatColumnEnd:-1,
repeatColumnStart:-1,
repeatRowEnd:-1,
repeatRowStart:-1,
rowEnd:24,
rowStart:0,
showBorder:false,
showColumnHeader:0,
showGridLine:false,
showRowHeader:0,
useMax:true,
watermark:[],
zoomFactor:1
}See also
4D View Pro Print Attributes
VP SET PRINT INFO
VP Get row attributes
VP Get row attributes ( rangeObj : Object ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of row properties |
Description
The VP Get row attributes command returns a collection of properties for any row in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of the rows whose attributes will be retrieved.
The returned collection contains any properties for the rows, whether or not they have been set by the VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES method.
Example
The following code returns a collection of the attributes within the given range:
var $range : Object
var $attr : Collection
$range:=VP Column("ViewProArea";1;2)
$attr:=VP Get row attributes($range)
See also
VP Get column attributes
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES
VP Get row count
VP Get row count ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area from object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Integer | <- | Total number of rows |
Description
The VP Get row count command returns the total number of rows from the designated sheet.
In vpAreaName, pass the name property of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can define where to get the row count in the optional sheetparameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
The following code returns the number of rows in the 4D View Pro area:
var $rowCount : Integer
$rowCount:=VP Get row count("ViewProarea")See also
VP Get column count
VP SET COLUMN COUNT
VP SET ROW COUNT
VP Get selection
VP Get selection ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area from object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of cells |
Description
The VP Get selection command returns a new range object referencing the current selected cells.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Example
The following code will retrieve the coordinates of all the cells in the current selection:
$currentSelection:=VP Get selection("myVPArea")
//returns a range object containing:
//$currentSelection.ranges[0].column=5
//$currentSelection.ranges[0].columnCount=2
//$currentSelection.ranges[0].row=8
//$currentSelection.ranges[0].rowCount=6See also
VP ADD SELECTION
VP Get active cell
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP Get sheet count
VP Get sheet count ( vpAreaName : Text ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| Function result | Integer | <- | Number of sheets |
Description
The VP Get sheet count command returns the number of sheets in the document loaded in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
Example
In the following document:

Get the sheet count and set the current sheet to the last sheet:
$count:=VP Get sheet count("ViewProArea")
//set the current sheet to the last sheet (indexing starts at 0)
VP SET CURRENT SHEET("ViewProArea";$count-1)
See also
VP Get sheet index
VP SET SHEET COUNT
VP Get sheet index
VP Get sheet index ( vpAreaName : Text ; name : Text ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| name | Text | -> | Sheet name |
| Function result | Integer | <- | Sheet index |
Description
The VP Get sheet index command returns the index of a sheet based on its name in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In name, pass the name of the sheet whose index will be returned. If no sheet named name is found in the document, the method returns -1.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
In the following document:

Get the index of the sheet called “Total first quarter”:
$index:=VP Get sheet index("ViewProArea";"Total first quarter") //returns 2See also
VP Get sheet count
VP Get sheet name
VP Get sheet name
VP Get sheet name ( vpAreaName : Text ; sheet : Integer ) : Text
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index |
| Function result | Text | <- | Sheet name |
Description
The VP Get sheet name command returns the name of a sheet based on its index in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In sheet, pass the index of the sheet whose name will be returned.
If the passed sheet index does not exist, the method returns an empty name.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
Get the name of the third sheet in the document:
$sheetName:=VP Get sheet name("ViewProArea";2)See also
VP Get sheet options
VP Get sheet options ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area from object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Sheet options object |
Description
The VP Get sheet options command returns an object containing the current sheet options of the vpAreaName area.
Pass the name of the 4D View Pro area in vpAreaName. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet (counting begins at 0). If omitted or if you pass vk current sheet, the current spreadsheet is used.
Returned object
The method returns an object containing the current values for all available sheet options. An option value may have been modified by the user or by the VP SET SHEET OPTIONSmethod.
To view the full list of the options, see Sheet Options.
Example
$options:=VP Get sheet options("ViewProArea")
If($options.colHeaderVisible) //column headers are visible
... //do something
End ifSee also
4D VIEW PRO SHEET OPTIONS
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS
VP Get show print lines
VP Get show print lines ( vpAreaName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) : Boolean
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | <- | Sheet index |
| Function result | Boolean | <- | True if print lines are visible, False otherwise |
Description
The VP Get show print lines command returns True if the print preview lines are visible and False if they are hidden.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If sheet is omitted, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
The following code checks if preview lines are displayed or hidden in the document:
var $result : Boolean
$result:=VP Get show print lines("ViewProArea";1)See also
VP Get spans
VP Get spans ( rangeObj : Object ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Object | <- | Object of cell spans in the defined range |
Description
The VP Get spans command retrieves the cell spans in the designated rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range of cell spans you want to retrieve. If rangeObj does not contain a cell span, an empty range is returned.
Example
You want to center the text for the spanned cells in this document:
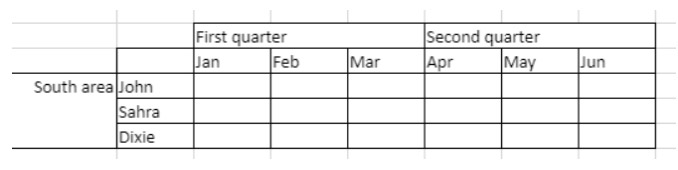
// Search for all cell spans
$range:=VP Get spans(VP All("ViewProArea"))
//center text
$style:=New object("vAlign";vk vertical align center;"hAlign";vk horizontal align center)
VP SET CELL STYLE($range;$style)See also
VP Get stylesheet
VP Get stylesheet ( vpAreaName : Text ; styleName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| styleName | Text | -> | Name of style |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
|Result|Object|<-|Style sheet object|
Description
The VP Get stylesheet command returns the styleName style sheet object containing the property values which have been defined.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In styleName, pass the name of the style sheet to get.
You can define where to get the style sheet in the optional sheetparameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Example
The following code:
$style:=VP Get stylesheet("ViewProArea";"GreenDashDotStyle")… will return the GreenDashDotStyle style object from the current sheet:
{
backColor:green,
borderBottom:{color:green,style:10},
borderLeft:{color:green,style:10},
borderRight:{color:green,style:10},
borderTop:{color:green,style:10}
}See also
4D View Pro Style Objects and Style Sheets
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP Get stylesheets
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET
VP Get stylesheets
VP Get stylesheets ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Target scope (default = current sheet) |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of style sheet objects |
Description
The VP Get stylesheets command returns the collection of defined style sheet objects from the designated sheet.
In vpAreaName, pass the name property of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can define where to get the style sheets in the optional sheet parameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Example
The following code will return a collection of all the style objects in the current sheet:
$styles:=VP Get stylesheets("ViewProArea")In this case, the current sheet uses two style objects:
[
{
backColor:green,
borderLeft:{color:green,style:10},
borderTop:{color:green,style:10},
borderRight:{color:green,style:10},
borderBottom:{color:green,style:10},
name:GreenDashDotStyle
},
{
backColor:red,
textIndent:10,
name:RedIndent
}
]See also
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP Get stylesheet
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET
VP Get table column attributes
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP Get table column index ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; columnName : Text {; sheet : Integer } ) : Integer
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| columnName | Text | -> | Name of the table column |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Integer | <- | Index of columnName |
Description
The VP Get table column index command returns the index of the columnName in the tableName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In columnName, pass the name of the table column for which you want to get the index.
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified or if you pass -1, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
If tableName or columnName is not found, the command returns -1.
Example
// Search the column id according the column name
var $id : Integer
$id:=VP Get table column index($area; $tableName; "Weight price")
// Remove the column by id
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS($area; $tableName; $id)See also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP Find table
VP Get table column attributes
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP Get table dirty rows
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R8 | Added |
VP Get table dirty rows ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text { ; reset : Boolean {; sheet : Integer }} ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| reset | Boolean | -> | True to clear the dirty status from the current table, False to keep it untouched. Default=True |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of objects with all the items modified since the last reset |
Description
The VP Get table dirty rows command returns a collection of dirty row objects, containing items that were modified since the last reset in the specified tableName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In tableName, pass the name of the table for which you want to get the dirty rows. Only modified columns bound to a data context will be taken into account.
By default, calling the command will clear the dirty status from the current table. To keep this status untouched, pass False in the reset parameter.
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified or if you pass -1, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
Each dirty row object in the returned collection contains the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| item | object | Modified object of the modified row |
| originalItem | object | Object before modification |
| row | integer | Index of the modified row |
If tableName is not found or if it does not contain a modified column, the command returns an empty collection.
Example
You want to count the number of edited rows:
var $dirty : Collection
$dirty:=VP Get table dirty rows("ViewProArea"; "ContextTable"; False)
VP SET NUM VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 0; 0); $dirty.length)See also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP Find table
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP RESIZE TABLE
VP Get table range
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP Get table range ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text {; onlyData : Integer {; sheet : Integer }} ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| onlyData | Integer | -> | vk table full range(default) or vk table data range |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range that contains the table |
Description
The VP Get table range command returns the range of tableName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In the onlyData parameter, you can pass one of the following constants to indicate if you want to get the data only:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
vk table full range |
0 | Get the cell range for the table area with footer and header (default if omitted) |
vk table data range |
1 | Get the cell range for the table data area only |
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
If tableName is not found, the command returns null.
See also
VP Get table theme
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R8 | Added |
VP Get table theme ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ) : cs.ViewPro.TableTheme
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| Result | cs.ViewPro.TableTheme | <- | Current table theme property values |
Description
The VP Get table theme command returns the current theme propertie values of the tableName. A table theme can be set using the VP CREATE TABLE or VP SET TABLE THEMEcommands, or through the interface.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area and in tableName, the name of the table.
The command returns an object of the cs.ViewPro.TableThemeclass with properties and values that describe the current table theme.
Example
The command returns a full theme object even if a native SpreadJS theme name was used to define the theme.
var $param : cs.ViewPro.TableTheme
$param:=cs.ViewPro.TableTheme.new()
$param.theme:="dark10" //use of a native theme name
VP SET TABLE THEME("ViewProArea"; "ContextTable"; $param)
$vTheme:=VP Get table theme("ViewProArea"; "ContextTable")
$result:=Asserted(Value type($vTheme.theme)=Is object) //trueSee also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP SET TABLE THEME
VP Get tables
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP Get tables ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Collection | <- | Text collection with all table names |
Description
The VP Get tables command returns a collection of all table names defined in the sheet.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
The following code will return a collection of all the table names in the current sheet:
$tables:=VP Get tables("ViewProArea")
//$tables contains for example ["contextTable","emailTable"]
See also
VP Get value
VP Get value ( rangeObj : Object ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Object | <- | Object containing a cell value |
Description
The VP Get value command retrieves a cell value from a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range whose value you want to retrieve.
Returned object
The object returned will contain the value property, and, in case of a js date value, a time property:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | Integer, Real, Boolean, Text, Date | Value in the rangeObj(except- time) |
| time | Real | Time value (in seconds) if the value is of the js date type |
If the object returned includes a date or time, it is treated as a datetime and completed as follows:
- time value – the date portion is completed as December 30, 1899 in dd/MM/yyyy format (30/12/1899)
- date value – the time portion is completed as midnight in HH:mm:ss format (00:00:00)
If rangeObj contains multiple cells or multiple ranges, the value of the first cell is returned. The command returns a null object if the cell is empty.
Example
$cell:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2)
$value:=VP Get value($cell)
If(Value type($value.value)=Is text)
VP SET TEXT VALUE($cell;New object("value";Uppercase($value.value))
End ifSee also
VP Get values
VP SET VALUE
VP SET VALUES
VP Get values
VP Get values ( rangeObj : Object ) : Collection
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| Result | Collection | <- | Collection of values |
Description
The VP Get values command retrieves the values from the designated rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range whose values you want to retrieve. If rangeObj includes multiple ranges, only the first range is used.
The collection returned by VP Get values contains a two-dimensional collection:
- Each element of the first-level collection represents a row and contains a subcollection of values
- Each subcollection contains cell values for the row. Values can be Integer, Real, Boolean, Text, Null. If a value is a date or time, it is returned in an object with the following properties:PropertyTypeDescriptionvalueDateValue in the cell (except- time)timeRealTime value (in seconds) if the value is of the js date type
Dates or times are treated as a datetime and completed as follows:
- time value – the date portion is completed as December 30, 1899
- date value – the time portion is completed as midnight (00:00:00:000)
Example
You want to get values from C4 to G6:
$result:=VP Get values(VP Cells("ViewProArea";2;3;5;3))
// $result[0]=[4,5,null,hello,world]
// $result[1]=[6,7,8,9,null]
// $result[2]=[null,{time:42,value:2019-05-29T00:00:00.000Z},null,null,null]See also
VP Get formulas
VP Get value
VP SET FORMULAS
VP SET VALUES
VP Get workbook options
VP Get workbook options ( vpAreaName : Text ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| Result | Object | <- | Object containing the workbook options |
Description
VP Get workbook options returns an object containing all the workbook options in vpAreaName
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
The returned object contains all the workbook options (default and modified ones), in the workbook.
The list of workbook options is referenced in VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS‘s description.
Example
var $workbookOptions : Object
$workbookOptions:=VP Get workbook options("ViewProArea")See also
I
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT ( vpAreaName : Text ; filePath : Text { ; paramObj : Object} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| filePath | Text | -> | Pathname of the document |
| paramObj | Object | -> | Import options |
Description
The VP IMPORT DOCUMENT command imports and displays the document designated by filePath in the 4D View Pro area vpAreaName. The imported document replaces any data already inserted in the area.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In filePath, pass the path and name of the document to be imported. The following formats are supported :
- 4D View Pro documents (extension “.4vp”)
- Microsoft Excel (extension “.xlsx”)
- text documents (extension “.txt”, “.csv”, the document must be in utf-8)
If the document extension is not a recognized extension, such as .4vp or .xlsx, the document is considered a text document. You must pass a full path, unless the document is located at the same level as the Project folder, in which case you can just pass its name.
When importing a Microsoft Excel-formatted file into a 4D View Pro document, some settings may be lost. You can verify your settings with this list from GrapeCity.
An error is returned if the filePath parameter is invalid, or if the file is missing or malformed.
The optional paramObj parameter allows you to define properties for the imported document:
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| formula | object | A callback method name to be launched when the import has completed. The method must use the Formulacommand. See Passing a callback method (formula). |
|
| password | text | Microsoft Excel only (optional) – The password used to protect a MS Excel document. | |
| csvOptions | object | options for csv import | |
| range | object | Cell range that contains the first cell where the data will be written. If the specified range is not a cell range, only the first cell of the range is used. | |
| rowDelimiter | text | Row delimiter. If not present, the delimiter is automatically determined by 4D. | |
| columnDelimiter | text | Column delimiter. Default: “,” |
For more information on the CSV format and delimiter-separated values in general, see this article on Wikipedia
Example 1
You want to import a default 4D View Pro document stored on the disk when the form is open:
C_TEXT($docPath)
If(Form event code=On VP Ready) //4D View Pro area loaded and ready
$docPath:="C:\\Bases\\ViewProDocs\\MyExport.4VP"
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT("VPArea";$docPath)
End ifExample 2
You want to import a password protected Microsoft Excel document into a 4D View Pro area:
$o:=New object
$o.password:="excel123"
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT("ViewProArea";"c:\\tmp\\excelfilefile.xlsx";$o)Example 3
You want to import a .txt file that uses a comma (“,”) as delimiter:

$params:=New object
$params.range:=VP Cells("ViewProArea";0;0;2;5)
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT("ViewProArea";"c:\\import\\my-file.txt";New object("csvOptions";$params))Here’s the result:
See also
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT
VP NEW DOCUMENT
VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT
VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT ( vpAreaName : Text { ; viewPro : Object} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| viewPro | Object | -> | 4D View Pro object |
Description
The VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT command imports and displays the viewPro 4D View Pro object in the vpAreaName 4D View Pro area. The imported object contents replaces any data already inserted in the area.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In viewPro, pass a valid 4D View Pro object. This object can have been created using VP Export to object or manually. For more information on 4D View Pro objects, please refer to the 4D View Pro object section.
An error is returned if the viewPro object is invalid.
Example
You want to import a spreadsheet that was previously saved in an object field:
QUERY([VPWorkBooks];[VPWorkBooks]ID=10)
VP IMPORT FROM OBJECT("ViewProArea1";[VPWorkBooks]SPBook)See also
VP INSERT COLUMNS
VP INSERT COLUMNS ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP INSERT COLUMNS command inserts columns into the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of the starting column (the column which designates where the new column will be inserted) and the number of columns to insert. If the number of column to insert is omitted (not defined), a single column is inserted.
New columns are inserted on the left, directly before the starting column in the rangeObj.
Example
To insert three columns before the second column:
VP INSERT COLUMNS(VP Column("ViewProArea";1;3))The results is:

See also
VP DELETE COLUMNS
VP DELETE ROWS
VP INSERT ROWS
VP INSERT ROWS
VP INSERT ROWS ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP INSERT ROWS command inserts rows defined by the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range of the starting row (the row which designates where the new row will be inserted) and the number of rows to insert. If the number of rows to insert is omitted (not defined), a single row is inserted.
New rows are inserted directly before the first row in the rangeObj.
Example
To insert 3 rows before the first row:
VP INSERT ROWS(VP Row("ViewProArea";0;3))The results is:

See also
VP DELETE COLUMNS
VP DELETE ROWS
VP INSERT COLUMNS
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName: Text ; column : Integer {; count : Integer {; insertAfter : Integer {; sheet : Integer }}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| column | Integer | -> | Index in the table of the starting column to insert |
| count | Text | -> | Number of columns to add (must be >0) |
| insertAfter | Integer | -> | vk table insert before or vk table insert aftercolumn |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS command inserts one or countempty column(s) in the specified tableName at the specified column index.
When a column has been inserted with this command, you typically modify its contents using the VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES command.
In the insertAfter parameter, you can pass one of the following constants to indicate if the column(s) must be inserted before or after the column index:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
vk table insert before |
0 | Insert column(s) before the column (default if omitted) |
vk table insert after |
1 | Insert column(s) after the column |
This command inserts some columns in the tableName table, NOT in the sheet. The total number of columns of the sheet is not impacted by the command. Data present at the right of the table (if any) are automatically moved right according to the number of added columns.
If tableName does not exist or if there is not enough space in the sheet, nothing happens.
Example
See examples for VP INSERT TABLE ROWS and VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES.
See also
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; row : Integer {; count : Integer {; insertAfter : Integer {; sheet : Integer }}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| row | Integer | -> | Index in the table of the starting row to insert |
| count | Text | -> | Number of rows to add (must be >0) |
| insertAfter | Integer | -> | vk table insert before or vk table insert afterrow |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP INSERT TABLE ROWS command inserts one or countempty row(s) in the specified tableName at the specified rowindex.
In the insertAfter parameter, you can pass one of the following constants to indicate if the row(s) must be inserted before or after the row index:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
vk table insert before |
0 | Insert row(s) before the row(default if omitted) |
vk table insert after |
1 | Insert row(s) after the row |
This command inserts some rows in the tableName table, NOT in the sheet. The total number of rows of the sheet is not impacted by the command. Data present below the table (if any) are automatically moved down according to the number of added rows.
If the tableName table is bound to a data context, the command inserts new, empty element(s) in the collection.
If tableName does not exist or if there is not enough space in the sheet, nothing happens.
Example
You create a table with a data context:
var $context : Object
$context:=New object()
$context.col:=New collection
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Smith"; "salary"; 10000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Wesson"; "salary"; 50000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Gross"; "salary"; 10500))
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $context)
VP CREATE TABLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 1; 1; 3; 3); "PeopleTable"; "col")
You want to insert two rows and two columns in the table, you can write:
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS("ViewProArea"; "PeopleTable"; 1; 2)
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS("ViewProArea"; "PeopleTable"; 1; 2)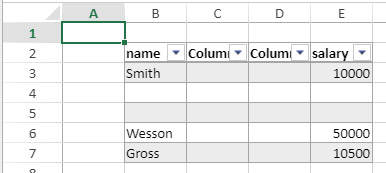
See also
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS
VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS
M
VP MOVE CELLS
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R4 | Added |
VP MOVE CELLS ( originRange : Object ; targetRange : Object ; options : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| originRange | Object | -> | Cell range to copy from |
| targetRange | Object | -> | Target range for the values, formatting and formulas |
| options | Object | -> | Additional options |
Description
The VP MOVE CELLS command moves or copies the values, style and formulas from originRange to targetRange.
originRange and targetRange can refer to different View Pro areas.
In originRange, pass a range object containing the values, style, and formula cells to copy or move. If originRange is a combined range, only the first one is used.
In targetRange, pass the range of cells where the cell values, style, and formulas will be copied or moved.
The options parameter has several properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| copy | Boolean | Determines if the values, formatting and formulas of the cells in originRange are removed after the command executes:False (default) to remove themTrue to keep them |
| pasteOptions | Longint | Specifies what is pasted. Possible values: ValueDescriptionvk clipboard options all(default)Pastes all data objects, including values, formatting, and formulas.vk clipboard options formattingPastes only the formatting.vk clipboard options formulasPastes only the formulas.vk clipboard options formulas and formattingPastes the formulas and formatting.vk clipboard options valuesPastes only the values.vk clipboard options value and formattingPastes the values and formatting. |
The paste options defined in the workbook options are taken into account.
Example
To copy the contents, values, formatting and formulas from an origin range:
var $originRange; $targetRange; $options : Object
$originRange:=VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 0; 0; 2; 5)
$targetRange:=VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 4; 0; 2; 5)
$options:=New object
$options.copy:=True
$options.pasteOptions:=vk clipboard options all
VP MOVE CELLS($originRange; $targetRange; $options)See also
VP Copy to object
VP PASTE FROM OBJECT
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS
N
VP Name
VP Name ( vpAreaName : Text ; rangeName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| rangeName | Text | -> | Existing range name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Range location (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of name |
Description
The VP Name command returns a new range object referencing a named range.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The rangeName parameter specifies an existing named cell range.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where rangeName is defined. If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet or the entire workbook with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Example
You want to give a value to the “Total” named range.
// name the B5 cell as Total
VP ADD RANGE NAME(VP Cell("ViewProArea";1;4);"Total")
$name:=VP Name("ViewProArea";" Total")
VP SET NUM VALUE($name;285;"$#,###.00")See also
VP ADD RANGE NAME
VP ALL
VP Cell
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Get names
VP REMOVE NAME
VP Row
VP NEW DOCUMENT
VP NEW DOCUMENT ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
Description
The VP NEW DOCUMENT command loads and display a new, default document in the 4D View Pro form area object vpAreaName. The new empty document replaces any data already inserted in the area.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Example
You want to display an empty document in the “myVPArea” form object:
VP NEW DOCUMENT("myVPArea")See also
O
VP Object to font
VP Object to font ( fontObj : Object ) : Text
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| fontObj | Object | -> | Font object |
| Result | Text | <- | Font shorthand |
Description
The VP Object to font command returns a font shorthand string from fontObj.
In fontObj, pass an object containing the font properties. The following properties are supported:
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| family | text | Specifies the font. | any standard or generic font family. Ex. “Arial”, “Helvetica”, “serif”, “arial,sans-serif” | Yes |
| size | text | Defines the size of the font.The line-height can be added to the font-size: font-size/line-height: Ex: “15pt/20pt” | a number with one of the following units: “em”, “ex”, “%”, “px”, “cm”, “mm”, “in”, “pt”, “pc”, “ch”, “rem”, “vh”, “vw”, “vmin”, “vmax”or one of the following:vk font size largevk font size largervk font size x largevk font size xx largevk font size smallvk font size smallervk font size x smallvk font size xx small |
Yes |
| style | text | The style of the font. | vk font style italicvk font style oblique |
No |
| variant | text | Specifies font in small capital letters. | vk font variant small caps |
No |
| weight | text | Defines the thickness of the font. | vk font weight 100vk font weight 200vk font weight 300vk font weight 400vk font weight 500vk font weight 600vk font weight 700vk font weight 800vk font weight 900vk font weight boldvk font weight boldervk font weight lighter |
No |
This object can be created with the VP Font to object command.
The returned shorthand string can be assigned to the “font” property of a cell with the VP SET CELL STYLE, for example.
Example
$cellStyle:=VP Get cell style($range)
$font:=VP Font to object($cellStyle.font)
$font.style:=vk font style oblique
$font.variant:=vk font variant small caps
$font.weight:=vk font weight bolder
$cellStyle.font:=VP Object to font($font)
//$cellStyle.font contains "bolder oblique small-caps 16pt arial"See also
4D View Pro Style Objects and Style Sheets
VP Font to object
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
P
VP PASTE FROM OBJECT
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R4 | Added |
VP PASTE FROM OBJECT ( rangeObj : Object ; dataObject : Object {; options : Longint} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Cell range object |
| dataObject | Object | -> | Object containing the data to be pasted |
| options | Longint | -> | Specifies what is pasted |
Description
The VP PASTE FROM OBJECT command pastes the contents, style and formulas stored in dataObject to the rangeObj object.
In rangeObj, pass the cell range object where the values, formatting, and/or formula cells will be pasted. If rangeObj refers to more than one cell, only the first one is used.
In dataObject, pass the object that contains the cell data, formatting, and formulas to be pasted.
In the optional options parameter, you can specify what to paste in the cell range. Possible values:
| Constant | Description | |
|---|---|---|
vk clipboard options all |
Pastes all data objects, including values, formatting, and formulas. | |
vk clipboard options formatting |
Pastes only the formatting. | |
vk clipboard options formulas |
Pastes only the formulas. | |
vk clipboard options formulas and formatting |
Pastes formulas and formatting. | |
vk clipboard options values |
Pastes only values. | |
vk clipboard options value and formatting |
Pastes values and formatting. |
The paste options defined in the workbook options are taken into account.
If options refers to a paste option not present in the copied object (e.g. formulas), the command does nothing.
Example
See example the example from VP Copy to object
See also
VP Copy to object
VP MOVE CELLS
VP Get workbook options
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS
VP PRINT
VP PRINT ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP PRINT command opens a print dialog window to print vpAreaName.
Pass the 4D View Pro area to be printed in vpAreaName. The command will open the system print dialog window where the printer can be specified and the page properties can be defined.
The properties defined in the print dialog window are for the printer paper, they are not the printing properties for the 4D View Pro area. Printing properties for 4D View Pro areas are defined using the VP SET PRINT INFO command. It is highly recommended that the properties for both the printer and the 4D View Pro area match, otherwise the printed document may not correspond to your expectations.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet to print (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current sheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet or entire workbook with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
- 4D View Pro areas can only be printed with the
VP PRINTcommand.- Commands from the 4D Printing language theme are not supported by
VP PRINT.- This command is intended for individual printing by the final end user. For automated print jobs, it is advised to export the 4D View Pro area as a PDF with the VP EXPORT DOCUMENT method.
Example
The following code:
VP PRINT("myVPArea")… will open a print dialog window:
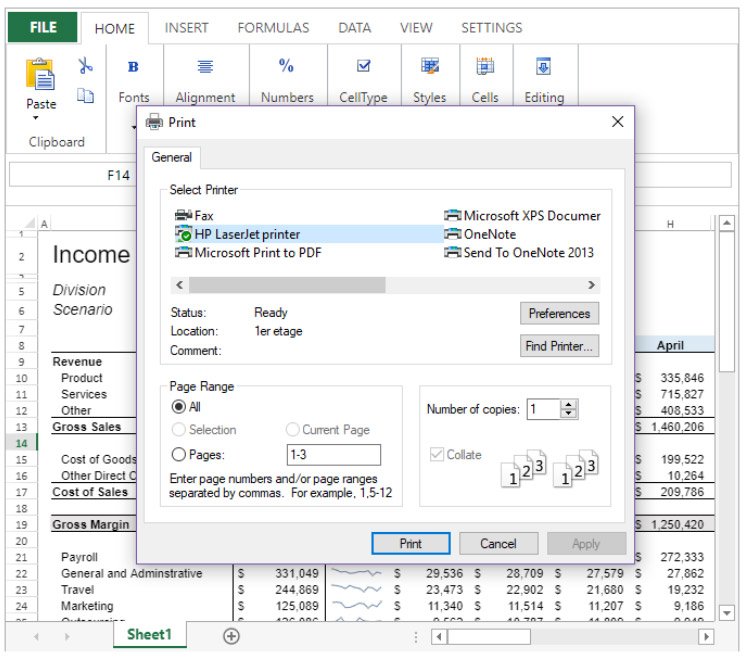
See also
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT
VP SET PRINT INFO
R
VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS
VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
Description
The VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS command immediately evaluates all formulas in vpAreaName. By default, 4D automatically computes formulas when they are inserted, imported, or exported. VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS allows you to force the compute at any time (e.g, in case modifications are made to the formulas or if the formulas contain calls to the database). The command launches the execution of the VP FLUSH COMMANDScommand to execute any stored commands and clear the command buffer, then calculates all formulas in the workbook.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Be sure the VP SUSPEND COMPUTING command has not been executed before using
VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS, otherwise the command does nothing.
Example
To refresh all formulas in the workbook:
VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS("ViewProArea")See also
VP RESUME COMPUTING
VP SUSPEND COMPUTING
VP REMOVE NAME
VP REMOVE NAME ( vpAreaName : Text ; name : Text { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| name | Text | -> | Name of the named range or named formula to remove |
| scope | Integer | -> | Target scope (default=current sheet) |
Description
The VP REMOVE NAME command removes the named range or named formula passed in the name parameter in the defined scope.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the named range or named formula that you want to remove in name.
You can define where to remove the name in scope using either the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Example
$range:=VP Cell("ViewProArea";0;0)
VP ADD RANGE NAME("Total1";$range)
VP REMOVE NAME("ViewProArea";"Total1")
$formula:=VP Get formula by name("ViewProArea";"Total1")
//$formula=nullSee also
VP REMOVE SHEET
VP REMOVE SHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; index: Integer )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| index | Integer | -> | Index of the sheet to remove |
See also
Description
The VP REMOVE SHEET command removes the sheet with the specified index from the document loaded in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In index, pass the index of the sheet to remove. If the passed index does not exist, the command does nothing.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
The document currently has three sheets:

Remove the third sheet:
VP REMOVE SHEET("ViewProArea";2)
VP REMOVE SPAN
VP REMOVE SPAN ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP REMOVE SPAN command removes the span from the cells in rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range object of the cell span. The spanned cells in the range are divided into individual cells.
Example
To remove all cell spans from this document:
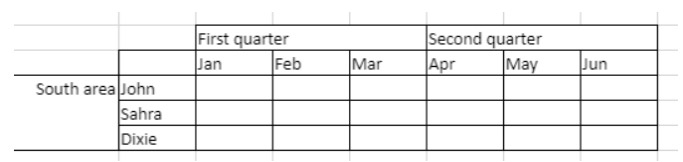
//find all cell spans
$span:=VP Get spans(VP All("ViewProArea"))
//remove the cell spans
VP REMOVE SPAN($span)Result:
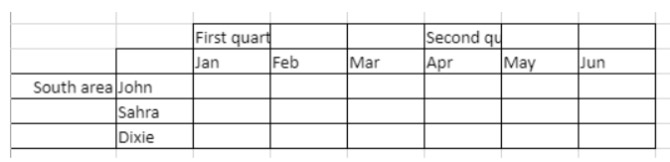
See also
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; styleName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| styleName | Text | -> | Name of style to remove |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP REMOVE STYLESHEET command removes the style sheet passed in the styleName from the vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the style sheet to remove in the styleName parameter.
You can define where to remove the style in the optional sheetparameter using the sheet index (counting begins at 0) or with the following constants:
vk current sheetvk workbook
Example
To remove the GreenDashDotStyle style object from the current sheet:
VP REMOVE STYLESHEET("ViewProArea";"GreenDashDotStyle")See also
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP Get stylesheet
VP Get stylesheets
VP REMOVE TABLE
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R6 | Added |
VP REMOVE TABLE ( vpAreaName : Object; tableName : Text {; options : Integer} {; sheet : Integer}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | View Pro area name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Name of the table to remove |
| options | Integer | -> | Additional options |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP REMOVE TABLE command removes a table that you created with VP CREATE TABLE.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the area where the table to remove is located.
In tableName, pass the name of the table to remove.
In options, you can specify additional behavior. Possible values are:
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vk table remove all | 0 | Remove all including style and data |
| vk table remove style | 1 | Remove style but keep data |
| vk table remove data | 2 | Remove data but keep style |
Table names are defined at sheet level. You can specify where the table is located using the optional sheet parameter (indexing starts at 0).
Example
To remove the “people” table in the second sheet and keep the data in the cells:
VP REMOVE TABLE("ViewProArea"; "people"; vk table remove style; 2)See also
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; column : Integer {; count : Integer {; sheet : Integer }}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| column | Integer | -> | Index in the table of the starting column to remove |
| count | Text | -> | Number of columns to remove (must be >0) |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS command removes one or count column(s) in the specified tableName at the specified column index. The command removes values and styles.
The command removes columns from the tableName table, NOT from the sheet. The total number of columns of the sheet is not impacted by the command. Data present at the right of the table (if any) are automatically moved letf according to the number of removed columns.
If tableName does not exist, nothing happens.
Example
To remove two columns from 3rd column of the “dataTable” table:
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS("ViewProArea"; "dataTable"; 3; 2)See also
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS
VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS
VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; row : Integer {; count : Integer {; sheet : Integer }}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| row | Integer | -> | Index in the table of the starting row to remove |
| count | Text | -> | Number of rows to remove (must be >0) |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS command removes one or countrow(s) from the specified tableName at the specified row index. The command removes values and styles.
This command removes rows from the tableName table, NOT from the sheet. The total number of rows of the sheet is not impacted by the command. Data present below the table (if any) are automatically moved up according to the number of removed rows.
If the tableName table is bound to a data context, the command removes element(s) from the collection.
If tableName does not exist, nothing happens.
Example
To remove two rows from 3rd row of the “dataTable” table:
VP REMOVE TABLE ROWS("ViewProArea"; "dataTable"; 3; 2)See also
VP INSERT TABLE ROWS
VP REMOVE TABLE COLUMNS
VP RESET SELECTION
VP RESET SELECTION ( vpAreaName : Text { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP RESET SELECTION command deselects all cells, resulting in no current selection or visible active cell.
A default active cell (cell A1) remains defined for 4D View Pro commands.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
You want to deselect all cells (the active cell and any selected cells):
VP RESET SELECTION("myVPArea")See also
VP ADD SELECTION
VP Get active cell
VP Get selection
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP RESIZE TABLE
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP RESIZE TABLE ( rangeObj : Object; tableName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | New range for the table |
| tableName | Text | -> | Name of the table |
Description
The VP RESIZE TABLE command changes the tableName size with regards to the rangeObj.
The following rules apply:
- Headers must remain in the same row and the resulting table range must overlap the original table range.
- If the row count of the resized table is inferior to the initial row count, values inside cropped rows or columns are kept if they were not bound to a data context, otherwise they are deleted.
- If the table expands on cells containing data:
- if rows are added, data is deleted,
- if columns are added, data are kept and are displayed in new columns.
If tableName does not exist, nothing happens.
Example
You create a table with a data context:
var $context : Object
$context:=New object()
$context.col:=New collection
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Smith"; "salary"; 10000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Wesson"; "salary"; 50000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Gross"; "salary"; 10500))
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $context)
VP CREATE TABLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 1; 1; 3; 3); "PeopleTable"; "col")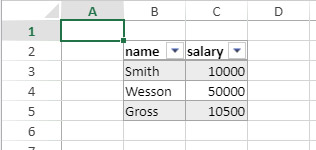
You want to add one column before and after the table as well as two empty rows. You can write:
VP RESIZE TABLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 0; 1; 4; 6); "PeopleTable")
See also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP Get table range
VP RESUME COMPUTING
VP RESUME COMPUTING ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
Description
The VP RESUME COMPUTING command restarts the calculation of formulas in vpAreaName.
The command reactivates the calculation service in 4D View Pro. Any formulas impacted by changes made while calculations were suspended are updated, and formulas added after VP RESUME COMPUTING is executed are calculated.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The 4D View Pro calculation service maintains a counter of suspend/resume actions. Therefore, each execution of
VP RESUME COMPUTINGmust be balanced by a corresponding execution of the VP SUSPEND COMPUTING command.
Example
See example in VP SUSPEND COMPUTING.
See also
VP RECOMPUTE FORMULAS
VP SUSPEND COMPUTING
VP Row
VP Row ( vpAreaName : Text; row : Integer { ; rowCount : Integer { ; sheet : Integer } } ) : Object
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| row | Integer | -> | Row index |
| rowCount | Integer | -> | Number of rows |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
| Result | Object | <- | Range object of row(s) |
Description
The VP Row command returns a new range object referencing a specific row or rows.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The row parameter defines the first row of the row range. Pass the row index (counting begins at 0) in this parameter. If the range contains multiple rows, you should also use the optional rowCount parameter.
The optional rowCount parameter allows you to define the total number of rows of the range. rowCount must be greater than 0. If omitted, the value will be set to 1 by default.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If not specified, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
You want to define a range object for the row shown below (on the current spreadsheet):
You can write:
$row:=VP Row("ViewProArea";9) // row 10See also
VP All
VP Cell
VP Cells
VP Column
VP Combine ranges
VP Name
VP ROW AUTOFIT
VP ROW AUTOFIT ( rangeObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP ROW AUTOFIT command automatically sizes the row(s) in rangeObj according to their contents.
In rangeObj, pass a range object containing a range of the rows whose size will be automatically handled.
Example
The following rows don’t correctly display the text:

VP ROW AUTOFIT(VP Row("ViewProArea";1;2))Result:

See also
VP Run offscreen area
VP Run offscreen area ( parameters : Object) : Mixed
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| parameters | Object | -> | Object containing the offscreen area’s attributes |
|Result |Mixed|<-|.result property of the .onEvent object, or Null if does not return a value|
Description
The VP Run offscreen area command creates an offscreen area in memory which can be used to process 4D View Pro area commands and functions.
In parameters object, pass any of the following optional properties. These properties will be available through the Thiscommand within the onEvent method and reference the instance:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| area | text | The name of the offscreen area. If omitted or null, a generic name is assigned (e.g., “OffscreenArea1”). |
|onEvent | object (formula)| A callback method that will be launched when the offscreen area is ready. It can be either:an onEvent function of a class, ora Formula objectBy default, the callback method is called on the On VP Ready, On Load, On Unload, On End URL Loading, On URL Loading Error, On VP Range Changed, or On Timer events. The callback method can be used to access the 4D View Pro form object variable.| |autoQuit | boolean | True (default value) if the command must stop the formula execution when the On End URL Loading or On URL Loading Error events occur.If false, you must use the CANCEL or ACCEPT commands in the onEventcallback method. | |timeout | number | Maximum time (expressed in seconds) before the area automatically closes if no event is generated. If set to 0, no limitation is applied. Default value: 60 | |result| mixed| Result of the processing (if any)| |\<customProperty> | mixed| Any custom attribute to be available in the onEvent callback method. |
The following property is automatically added by the command if necessary:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| timeoutReached | boolean | Added with true value if timeout has been exceeded |
The offscreen area is only available during the execution of the
VP Run offscreen areacommand. It will automatically be destroyed once execution has ended.
The following commands can be used in the callback method:
ACCEPTCANCELSET TIMERWA Evaluate JavaScriptWA EXECUTE JAVASCRIPT FUNCTION
Example 1
You want to create an offscreen 4D View Pro area and get the value of a cell:
// cs.OffscreenArea class declaration
Class constructor ($path : Text)
This.filePath:=$path
// This function will be called on each event of the offscreen area
Function onEvent()
Case of
:(FORM Event.code=On VP Ready)
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT(This.area;This.filePath)
This.result:=VP Get value(VP Cell(This.area;6;22))
ALERT("The G23 cell contains the value: "+String(This.result))
End caseThe OffscreenArea callback method:
$o:=cs.OffscreenArea.new()
$result:=VP Run offscreen area($o)Example 2
You want to load a large document offscreen, wait for all calculations to complete evaluating, and export it as a PDF:
//cs.OffscreenArea class declaration
Class constructor($pdfPath : Text)
This.pdfPath:=$pdfPath
This.autoQuit:=False
This.isWaiting:=False
Function onEvent()
Case of
:(FORM Event.code=On VP Ready)
// Document import
VP IMPORT DOCUMENT(This.area;$largeDocument4VP)
This.isWaiting:=True
// Start a timer to verify if all calculations are finished.
// If during this period the "On VP Range Changed" is thrown, the timer will be restarted
// The time must be defined according to the computer configuration.
SET TIMER(60)
:(FORM Event.code=On VP Range Changed)
// End of calculation detected. Restarts the timer
If(This.isWaiting)
SET TIMER(60)
End if
:(FORM Event.code=On Timer)
// To be sure to not restart the timer if you call others 4D View command after this point
This.isWaiting:=False
// Stop the timer
SET TIMER(0)
// Start the PDF export
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT(This.area;This.pdfPath;New object("formula";Formula(ACCEPT)))
:(FORM Event.code=On URL Loading Error)
CANCEL
End caseThe OffscreenArea callback method:
$o:=cs.OffscreenArea.new()
$result:=VP Run offscreen area($o)See also
Blog post: End of document loading
S
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET ACTIVE CELL ( rangeObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
Description
The VP SET ACTIVE CELL command defines a specified cell as active.
In rangeObj, pass a range containing a single cell as an object (see VP Cell). If rangeObj is not a cell range or contains multiple ranges, the first cell of the first range is used.
Example
To set the cell in column D, row 5 as the active cell:
$activeCell:=VP Cell("myVPArea";3;4)
VP SET ACTIVE CELL($activeCell)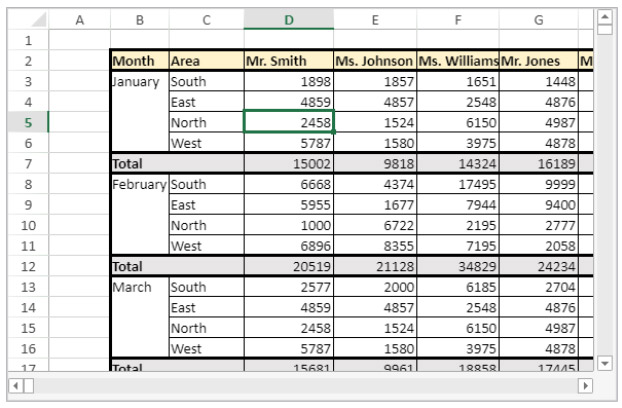
See also
VP ADD SELECTION
VP Get active cell
VP Get selection
VP RESET SELECTION
VP SET SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP SET ALLOWED METHODS
VP SET ALLOWED METHODS ( methodObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodObj | Object | -> | Allowed methods in the 4D View Pro areas |
Compatibility
For greater flexiblity, it is recommended to use the
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONScommand which allows you to designate 4D formulas that can be called from 4D View Pro areas. As soon asVP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSis called,VP SET ALLOWED METHODScalls are ignored. 4D View Pro also supports 4D’s genericSET ALLOWED METHODScommand if neitherVP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSnorVP SET ALLOWED METHODSare called, however using the generic command is not recommended.
Description
The VP SET ALLOWED METHODS command designates the project methods that can be called in 4D View Pro formulas. This command applies to all 4D View Pro areas initialized after its call during the session. It can be called multiple times in the same session to initialize different configurations.
By default for security reasons, if you do not execute the VP SET ALLOWED METHODS command, no method call is allowed in 4D View Pro areas — except if 4D’s generic SET ALLOWED METHODScommand was used (see compatibility note). Using an unauthorized method in a formula prints a #NAME? error in the 4D View Pro area.
In the methodObj parameter, pass an object in which each property is the name of a function to define in the 4D View Pro areas:
| Property | Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
<functionName> |
Object | Custom function definition. The <functionName>property name defines the name of the custom function to display in 4D View Pro formulas (no spaces allowed) |
||
| method | Text | (mandatory) Name of the existing 4D project method to allow | ||
| parameters | Collection of objects | Collection of parameters (in the order they are defined in the method). | ||
| [].name | Text | Name of a parameter to display for the <functionName>.Note: Parameter names must not contain space characters. |
||
| [].type | Number | Type of the parameter. Supported types:Is BooleanIs dateIs IntegerIs objectIs realIs textIs timeIf omitted, by default the value is automatically sent with its type, except date or time values which are sent as an object (see Parameters section). If type is Is object, the object has the same structure as the object returned by VP Get value. |
||
| summary | Text | Function description to display in 4D View Pro | ||
| minParams | Number | Minimum number of parameters | ||
| maxParams | Number | Maximum number of parameters. Passing a number higher than the length of parameters allows declaring “optional” parameters with default type |
Example
You want to allow two methods in your 4D View Pro areas:
C_OBJECT($allowed)
$allowed:=New object //parameter for the command
$allowed.Hello:=New object //create a first simple function named "Hello"
$allowed.Hello.method:="My_Hello_Method" //sets the 4D method
$allowed.Hello.summary:="Hello prints hello world"
$allowed.Byebye:=New object //create a second function with parameters named "Byebye"
$allowed.Byebye.method:="My_ByeBye_Method"
$allowed.Byebye.parameters:=New collection
$allowed.Byebye.parameters.push(New object("name";"Message";"type";Is text))
$allowed.Byebye.parameters.push(New object("name";"Date";"type";Is date))
$allowed.Byebye.parameters.push(New object("name";"Time";"type";Is time))
$allowed.Byebye.summary:="Byebye prints a custom timestamp"
$allowed.Byebye.minParams:=3
$allowed.Byebye.maxParams:=3
VP SET ALLOWED METHODS($allowed)After this code is executed, the defined functions can be used in 4D View Pro formulas:
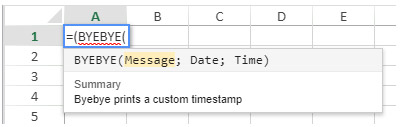
In 4D View Pro formulas, function names are automatically displayed in uppercase.
See also
4D functions
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS
VP SET BINDING PATH
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R5 | Added |
VP SET BINDING PATH ( rangeObj : Object ; dataContextAttribute : Text)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| dataContextAttribute | Text | -> | Name of the attribute to bind to rangeObj |
Description
The VP SET BINDING PATH command binds an attribute from a sheet’s data context to rangeObj. After you set a data context using the SET DATA CONTEXT method. When loaded, if the data context contains the attribute, the value of dataContextAttribute is automatically displayed in the cells in rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object that is either a cell range or a combined range of cells.
- If rangeObj is a range with several cells, the command binds the attribute to the first cell of the range.
- If rangeObj contains several ranges of cells, the command binds the attribute to the first cell of each range.
In dataContextAttribute, pass the name of the attribute to bind to rangeObj. If dataContextAttribute is an empty string, the function removes the current binding.
Attributes of type collection are not supported. When you pass the name of a collection attribute, the command does nothing.
Example
Set a data context and bind the firstName and lastNameattribute to cells:
var $p : Object
$p:=New object
$p.firstName:="Freehafer"
$p.lastName:="Nancy"
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $p)
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 0; 0); "firstName")
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 1; 0); "lastName")
See also
VP Get binding path
VP Get data context
VP SET DATA CONTEXT
VP SET BOOLEAN VALUE
VP SET BOOLEAN VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; boolValue : Boolean)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| boolValue | Boolean | -> | Boolean value to set |
Description
The VP SET BOOLEAN VALUE command assigns a specified boolean value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The boolValue parameter allows you to pass the boolean value (True or False) that will be assigned to the rangeObj.
Example
//Set the cell value as False
VP SET BOOLEAN VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);False)See also
VP SET BORDER
VP SET BORDER ( rangeObj : Object ; borderStyleObj : Object ; borderPosObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| borderStyleObj | Object | -> | Object containing border line style |
| borderPosObj | Object | -> | Object containing border placement |
Description
The VP SET BORDER command applies the border style(s) defined in borderStyleObj and borderPosObj to the range defined in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range of cells where the border style will be applied. If the rangeObj contains multiple cells, borders applied with VP SET BORDER will be applied to the rangeObj as a whole (as opposed to the VP SET CELL STYLE command which applies borders to each cell of the rangeObj). If a style sheet has already been applied, VP SET BORDER will override the previously applied border settings for the rangeObj.
The borderStyleObj parameter allows you to define the style for the lines of the border. The borderStyleObj supports the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| color | text | Defines the color of the border. Default = black. | CSS color “#rrggbb” syntax (preferred syntax), CSS color “rgb(r,g,b)” syntax (alternate syntax), CSS color name (alternate syntax) |
| style | Integer | Defines the style of the border. Default = empty. | vk line style dash dotvk line style dash dot dotvk line style dashedvk line style dottedvk line style doublevk line style emptyvk line style hairvk line style mediumvk line style medium dash dotvk line style medium dash dot dotvk line style medium dashedvk line style slanted dash dotvk line style thickvk line style thin |
You can define the position of the borderStyleObj (i.e., where the line is applied) with the borderPosObj:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| all | boolean | Border line style applied to all borders. |
| left | boolean | Border line style applied to left border. |
| top | boolean | Border line style applied to top border. |
| right | boolean | Border line style applied to right border. |
| bottom | boolean | Border line style applied to bottom border. |
| outline | boolean | Border line style applied to outer borders only. |
| inside | boolean | Border line style applied to inner borders only. |
| innerHorizontal | boolean | Border line style applied to inner horizontal borders only. |
| innerVertical | boolean | Border line style applied to inner vertical borders only. |
Example 1
This code produces a border around the entire range:
$border:=New object("color";"red";"style";vk line style thick)
$option:=New object("outline";True)
VP SET BORDER(VP Cells("ViewProArea";1;1;3;3);$border;$option)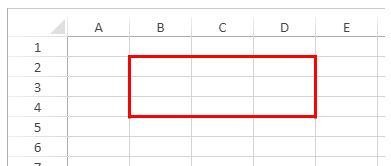
Example 2
This code demonstrates the difference between VP SET BORDER and setting borders with the VP SET CELL STYLEcommand:
// Set borders using VP SET BORDER
$border:=New object("color";"red";"style";vk line style thick)
$option:=New object("outline";True)
VP SET BORDER(VP Cells("ViewProArea";1;1;3;3);$border;$option)
// // Set borders using VP SET CELL STYLE
$cellStyle:=New object
$cellStyle.borderBottom:=New object("color";"blue";"style";vk line style thick)
$cellStyle.borderRight:=New object("color";"blue";"style";vk line style thick)
VP SET CELL STYLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea";4;4;3;3);$cellStyle)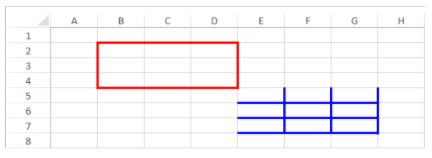
See also
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP SET CELL STYLE ( rangeObj : Object ; styleObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| styleObj | Object | -> | Style object |
Description
The VP SET CELL STYLE command applies the style(s) defined in the styleObj to the cells defined in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range of cells where the style will be applied. If the rangeObj contains multiple cells, the style is applied to each cell.
Borders applied with
VP SET CELL STYLEwill be applied to each cell of the rangeObj, as opposed to the VP SET BORDER command which applies borders to the rangeObjas a whole.
The styleObj parameter lets you pass an object containing style settings. You can use an existing style sheet or create a new style. If the styleObj contains both an existing style sheet and additional style settings, the existing style sheet is applied first, followed by the additional settings.
To remove a style and revert to the default style settings (if any), pass a NULL value:
- giving the styleObj parameter a NULL value will remove any style settings from the rangeObj,
- giving an attribute a NULL value will remove this specific attribute from the rangeObj.
For more information about style objects and style sheets, see the Style Objects paragraph.
Example
$style:=New object
$style.font:="8pt Arial"
$style.backColor:="Azure"
$style.foreColor:="red"
$style.hAlign:=1
$style.isVerticalText:=True
$style.borderBottom:=New object("color";"#800080";"style";vk line style thick)
$style.backgroundImage:=Null //remove a specific attribute
VP SET CELL STYLE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";1;1);$style)
See also
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP Font to object
VP Get cell style
VP Object to font
VP SET BORDER
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES ( rangeObj : Object ; propertyObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| propertyObj | Object | -> | Object containing column properties |
Description
The VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES command applies the attributes defined in the propertyObj to the columns in the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass an object containing a range. If the range contains both columns and rows, attributes are applied only to the columns.
The propertyObj parameter lets you specify the attributes to apply to the columns in the rangeObj. These attributes are:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| width | number | Column width expressed in pixels |
| pageBreak | boolean | True to insert a page break before the first column of the range, else false |
| visible | boolean | True if the column is visible, else false |
| resizable | boolean | True if the column can be resized, else false |
| header | text | Column header text |
Example
To change the size of the second column and set the header, you write:
C_OBJECT($column;$properties)
$column:=VP Column("ViewProArea";1) //column B
$properties:=New object("width";100;"header";"Hello World")
VP SET COLUMN ATTRIBUTES($column;$properties)
See also
VP Column
VP Get column attributes
VP Get row attributes
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES
VP SET COLUMN COUNT
VP SET COLUMN COUNT ( vpAreaName : Text , columnCount : Integer { , sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| columnCount | Integer | -> | Number of columns |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET COLUMN COUNT command defines the total number of columns in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the total number of columns in the columnCountparameter. columnCount must be greater than 0.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the columnCount will be applied (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
The following code defines five columns in the 4D View Pro area:
VP SET COLUMN COUNT("ViewProArea";5)
See also
VP Get column count
VP Get row count
VP SET ROW COUNT
VP SET CURRENT SHEET
VP SET CURRENT SHEET ( vpAreaName : Text ; sheet : Integer)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| sheet | Integer | <- | Index of the new current sheet |
Description
The VP SET CURRENT SHEET command sets the current sheet in vpAreaName . The current sheet is the selected sheet in the document.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In sheet, pass the index of the sheet to be set as current sheet. If the index passed is inferior to 0 or exceeds the number of sheets, the command does nothing.
Indexing starts at 0.
Example
The document’s current sheet is the first sheet:

Set the current sheet to the third sheet:
VP SET CURRENT SHEET("ViewProArea";2)
See also
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS ( vpAreaName : Text ; formulaObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| formulaObj | Object | -> | Formula object |
Description
The VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS command designates the 4D formulas that can be called directly from 4D View Pro formulas. Because custom functions are not stored in the document,VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS must be executed in the On Load form event.
The formulas specified by VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS appear in a pop-up menu when the first letter of their name is entered. See the Formulas and Functions page.
If
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSis called multiple times for the same area, in the same session, only the last call is taken into account.
Pass the name of the 4D View Pro area in vpAreaName. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In the formulaObj parameter, pass an object containing the 4D formulas that can be called from 4D View Pro formulas as well as additional properties. Each customFunction property passed in formulaObj becomes the name of a function in the 4D View Pro area.
| Property | Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
<customFunction> |
Object | Custom function definition. <customFunction>defines the name of the custom function to display in 4D View Pro formulas (no spaces allowed) |
||
| formula | Object | 4D formula object (mandatory). See the Formulacommand. |
||
| parameters | Collection of objects | Collection of parameters (in the order they are defined in the formula) | ||
| [].name | Text | Name of parameter to display in 4D View Pro | ||
| [].type | Number | Type of the parameter. Supported types:Is BooleanIs dateIs IntegerIs objectIs realIs textIs timeIf type is omitted or if the default value (-1) is passed, the value is automatically sent with its type, except date or time values which are sent as an object (see Parameterssection).If type is Is object, the object has the same structure as the object returned by VP Get value. |
||
| summary | Text | Formula description to display in 4D View Pro | ||
| minParams | Number | Minimum number of parameters | ||
| maxParams | Number | Maximum number of parameters. Passing a number higher than the length of parameters allows declaring “optional” parameters with default type |
WARNING
- As soon as
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSis called, the methods allowed by the VP SET ALLOWED METHODScommand (if any) are ignored in the 4D View Pro area.- As soon as
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONSis called, the functions based uponSET TABLE TITLESandSET FIELD TITLEScommands are ignored in the 4D View Pro area.
Example
You want to use formula objects in a 4D View Pro area to add numbers, retrieve a customer’s last name and gender:
Case of
:(FORM Event.code=On Load)
var $o : Object
$o:=New object
// Define "addnum" function from a method named "addnum"
$o.addnum:=New object
$o.addnum.formula:=Formula(addnum)
$o.addnum.parameters:=New collection
$o.addnum.parameters.push(New object("name";"num1";"type";Is Integer))
$o.addnum.parameters.push(New object("name";"num2";"type";Is Integer))
// Define "ClientLastName" function from a database field
$o.ClientLastName:=New object
$o.ClientLastName.formula:=Formula([Customers]lastname)
$o.ClientLastName.summary:="Lastname of the current client"
// Define "label" function from a 4D expression with one parameter
$o.label:=New object
$o.label.formula:=Formula(ds.Customers.get($1).label)
$o.label.parameters:=New collection
$o.label.parameters.push(New object("name";"ID";"type";Is Integer))
// Define "Title" function from a variable named "Title"
$o.Title:=New object
$o.Title.formula:=Formula(Title)
VP SET CUSTOM FUNCTIONS("ViewProArea";$o)
End caseSee also
VP SET DATA CONTEXT
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R5 | Added |
VP SET DATA CONTEXT ( vpAreaName : Text ; dataObj : Object {; options : Object } {; sheet : Integer} )
VP SET DATA CONTEXT ( vpAreaName : Text ; dataColl : Collection ; {options : Object } {; sheet : Integer} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Object | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| dataObj | Object | -> | Data object to load in the data context |
| dataColl | Object | -> | Data collection to load in the data context |
| options | Object | -> | Additional options |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index |
Description
The VP SET DATA CONTEXT command sets the data context of a sheet. A data context is an object or a collection bound to a worksheet, and whose contents can be used to automatically fill the sheet cells, either by using an autogenerate option or the VP SET BINDING PATH method. On the other hand, the VP Get data context command can return a context containing user modifications.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
In dataObj or dataColl, pass an object or a collection containing the data to load in the data context. Images are converted to data URI schemes.
To pass a time value in dataObj or dataColl, encapsulate it in an object with the following properties (see example 4):
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | Integer, Real, Boolean, Text, Date, Null | Value to put in the context |
| time | Real | Time value (in seconds) to put in the context |
In options, you can pass an object that specifies additional options. Possible properties are:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reset | Object | True to reset the sheet’s contents before loading the new context, False (default) otherwise. |
| autoGenerateColumns | Object | Only used when data is a collection. True (default) to specify that columns must be generated automatically when the data context is bound. In this case, the following rules apply: If dataColl is a collection of objects, attribute names are used as column titles (see example 2).If dataColl contains subcollections of scalar values, each subcollection defines the values in a row (see example 3). The first subcollection determines how many columns are created. |
In sheet, pass the index of the sheet that will receive the data context. If no index is passed, the context is applied to the current sheet.
If you export your document to an object using VP Export to object, or to a 4DVP document using VP EXPORT DOCUMENT, the includeBindingSource option lets you copy the contents of the current contexts as cell values in the exported object or document. For more details, refer to the description of those methods.
Example
Pass an object and bind the context data to cells in the first row:
var $data : Object
$data:=New object
$data.firstName:="Freehafer"
$data.lastName:="Nancy"
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $data)
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 0; 0); "firstName")
VP SET BINDING PATH(VP Cell("ViewProArea"; 1; 0); "lastName")

Example 2
Pass a collection of objects and generate columns automatically:
var $options : Object
var $data : Collection
$data:=New collection()
$data.push(New object("firstname"; "John"; "lastname"; "Smith"))
$data.push(New object("firstname"; "Mary"; "lastname"; "Poppins"))
$options:=New object("autoGenerateColumns"; True)
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $data; $options)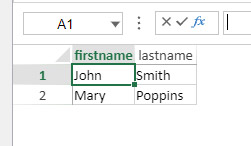
Example 3
The data passed as a parameter is a collection that contains subcollections. Each subcollection defines the contents of a row:
var $data : Collection
var $options : Object
$data:=New collection
$data.push(New collection(1; 2; 3; False; "")) // 5 columns are created
$data.push(New collection) // Second row is empty
$data.push(New collection(4; 5; Null; "hello"; "world")) // Third row has 5 values
$data.push(New collection(6; 7; 8; 9)) // Fourth row has 4 values
$options:=New object("autoGenerateColumns"; True)
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $data; $options)
Example 4 – Date and time syntax
var $data : Collection
var $options : Object
$data:= New collection()
// Dates can be passed as scalar values
$data.push(New collection("Date"; Current date))
// Time values must be passed as object attributes
$data.push(New collection("Time"; New object("time"; 5140)))
// Date + time example
$data.push(New collection("Date + Time"; New object("value"; Current date; "time"; 5140)))
$options:=New object("autoGenerateColumns"; True)
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $data; $options)Here’s the result once the columns are generated:
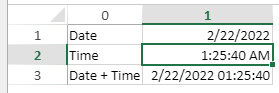
See also
VP SET BINDING PATH
VP Get binding path
VP Get data context
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; dateValue : Date ; timeValue : Time {; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| dateValue | Date | -> | Date value to set |
| timeValue | Time | -> | Time value to set |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of value |
Description
The VP SET DATE TIME VALUE command assigns a specified date and time value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The dateValue parameter specifies a date value to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The timeValue parameter specifies a time value (expressed in seconds) to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the dateValueand timeValue parameters. For information on patterns and formatting characters, please refer to the Date and time formatssection.
Example
//Set the cell value as the current date and time
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";6;2);Current time;Current date;vk pattern full date time)
//Set the cell value as the 18th of December
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;9);!2024-12-18!;?14:30:10?;vk pattern sortable date time)See also
4D View Pro cell format
VP SET DATE VALUE
VP SET TIME VALUE
VP SET VALUE
VP SET DATE VALUE
VP SET DATE VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; dateValue : Date { ; formatPattern : Text } )
|Parameter|Type||Description|
|—|—|—|—| |rangeObj |Object|->|Range object| |dateValue |Date|->|Date value to set| |formatPattern |Text|->|Format of value|
Description
The VP SET DATE VALUE command assigns a specified date value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The dateValue parameter specifies a date value to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the dateValueparameter. Pass any custom format or you can use one of the following constants:
| Constant | Description | Default US pattern |
|---|---|---|
vk pattern long date |
ISO 8601 format for the full date | “dddd, dd MMMM yyyy” |
vk pattern month day |
ISO 8601 format for the month and day | “MMMM dd” |
vk pattern short date |
Abbreviated ISO 8601 format for the date | “MM/dd/yyyy” |
vk pattern year month |
ISO 8601 format for the month and year | “yyyy MMMM” |
For information on patterns and formatting characters, please refer to the Date and time formats section.
Example
//Set the cell value to the current date
VP SET DATE VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";4;2);Current date))
//Set the cell value to a specific date with a designated format
VP SET DATE VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";4;4);Date("12/25/94");"d/m/yy ")
VP SET DATE VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";4;6);!2005-01-15!;vk pattern month day)See also
4D View Pro cell format
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE
VP SET VALUE
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE ( vpAreaName : Text ; styleObj : Object { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| styleObj | Object | -> | Style object |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (default = current sheet) |
Description
The VP SET DEFAULT STYLE command defines the style in the styleObj as the default style for a sheet.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The styleObj lets you pass an object containing style settings. You can use an existing style sheet or you can create a new style. For more information, see the Style objects paragraph.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the style will be defined. If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
$style:=New object
$style.hAlign:=vk horizontal align left
$style.font:="12pt papyrus"
$style.backColor:="#E6E6FA" //light purple color
VP SET DEFAULT STYLE("myDoc";$style)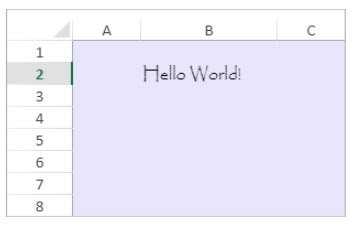
See also
VP ADD STYLESHEET
VP Font to object
VP Get default style
VP Object to font
VP SET BORDER
VP SET CELL STYLE
VP SET FIELD
VP SET FIELD ( rangeObj : Object ; field : Pointer { ; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| field | Pointer | -> | Reference to field in virtual structure |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of field |
Description
The VP SET FIELD command assigns a 4D database virtual field to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the specified field will be linked in each cell.
The field parameter specifies a 4D database virtual field to be assigned to the rangeObj. The virtual structure name for fieldcan be viewed in the formula bar. If any of the cells in rangeObjhave existing content, it will be replaced by field.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the fieldparameter. You can pass any valid custom format.
Example
VP SET FIELD(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);->[TableName]Field)See also
VP SET FORMULA
VP SET FORMULA ( rangeObj : Object ; formula : Text { ; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| formula | Text | -> | Formula or 4D method |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of field |
Description
The VP SET FORMULA command assigns a specified formula or 4D method to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the formula specified will be linked in each cell.
The formula parameter specifies a formula or 4D method name to be assigned to the rangeObj.
If the formula is a string, use the period
.as numerical separator and the comma,as parameter separator. If a 4D method is used, it must be allowed with theVP SET ALLOWED METHODScommand.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the formula.
You remove the formula in rangeObj by replacing it with an empty string (“”).
Example 1
VP SET FORMULA(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);"SUM($A$1:$C$10)")Example 2
To remove the formula:
VP SET FORMULA(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);"")Example 3
VP SET FORMULA($range;"SUM(A1,B7,C11)") //"," to separate parametersSee also
Cell format
VP Get Formula
VP SET FORMULAS
VP SET VALUE
VP SET FORMULAS
VP SET FORMULAS ( rangeObj : Object ; formulasCol : Collection )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Cell range object |
| formulasCol | Collection | -> | Collection of formulas |
Description
The VP SET FORMULAS command assigns a collection of formulas starting at the specified cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell (created with VP Cell) whose formula you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple ranges, only the first range is used.
The formulasCol is a two-dimensional collection:
- The first-level collection contains subcollections of formulas. Each subcollection defines a row.
- Each subcollection defines cell values for the row. Values must be text elements containing the formulas to assign to the cells.
If the formula is a string, use the period
.as numerical separator and the comma,as parameter separator. If a 4D method is used, it must be allowed with theVP SET ALLOWED METHODScommand.
You remove the formulas in rangeObj by replacing them with an empty string (“”).
Example 1
$formulas:=New collection
$formulas.push(New collection("MAX(B11,C11,D11)";"myMethod(G4)")) // First row
$formulas.push(New collection("SUM(B11:D11)";"AVERAGE(B11:D11)")) // Second row
VP SET FORMULAS(VP Cell("ViewProArea";6;3);$formulas) // Set the cells with the formulasmyMethod:
$0:=$1*3.33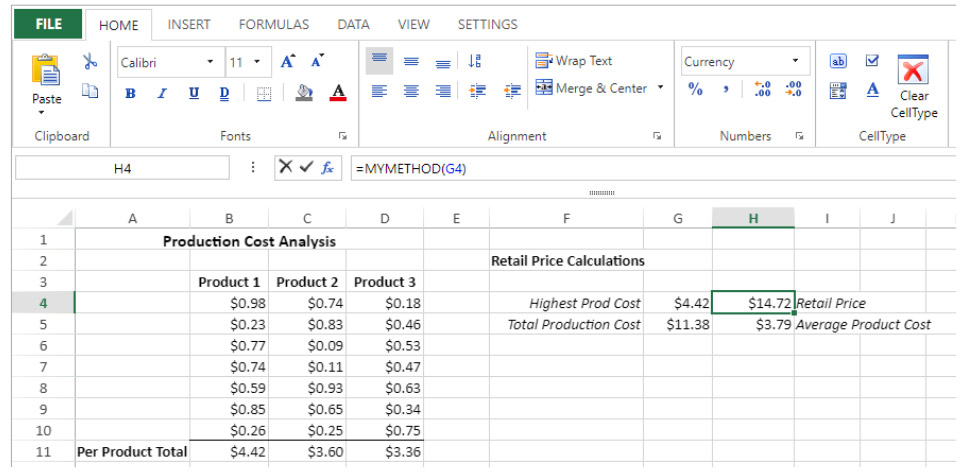
Example 2
To remove formulas:
$formulas:=New collection
$formulas.push(New collection("";"")) // first collection
$formulas.push(New collection("";"")) // second collection
VP SET FORMULAS(VP Cell("ViewProArea";0;0);$formulas) // Assign to cellsSee also
VP Get Formulas
VP GET VALUESVP SET FORMULA
VP SET VALUES
VP SET FROZEN PANES
VP SET FROZEN PANES ( vpAreaName : Text ; paneObj : Object { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| paneObj | Object | -> | Object containing frozen column and row information |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET FROZEN PANES command sets the frozen status of the columns and rows in the paneObj so they are always displayed in the vpAreaName. Frozen columns and rows are fixed in place and do not move when the rest of the document is scrolled. A solid line is displayed to indicate that columns and rows are frozen. The location of the line depends on where the frozen column or row is on the sheet:
- Columns on the left or right: For columns on the left of the sheet, the line is displayed on the right side of the last frozen column. For columns on the right side of the sheet, the line is displayed on the left side of the first frozen column.
- Rows on the top or bottom: For rows at the top of the sheet, the line is displayed below the last frozen row. For rows at the bottom of the sheet, the line is displayed above the first frozen row.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can pass an object defining the columns and rows to freeze in the paneObj parameter. Setting the value of any of the column or row properties equal to zero resets (unfreezes) the property. If a property is set to less than zero, the command does nothing. You can pass:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|
|columnCount | Integer | The number of frozen columns on the left of the sheet| |trailingColumnCount |Integer | The number of frozen columns on the right of the sheet |rowCount | Integer | The number of frozen rows on the top of the sheet | |trailingRowCount | Integer | The number of frozen rows on the bottom of the sheet|
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the range will be defined (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
You want to freeze the first three columns on the left, two columns on the right, and the first row:
C_OBJECT($panes)
$panes:=New object
$panes.columnCount:=3
$panes.trailingColumnCount:=2
$panes.rowCount:=1
VP SET FROZEN PANES("ViewProArea";$panes)
See also
VP SET NUM VALUE
VP SET NUM VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; numberValue : Number { ; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| numberValue | Number | -> | Number value to set |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of value |
Description
The VP SET NUM VALUE command assigns a specified numeric value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The numberValue parameter specifies a numeric value to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the numberValue parameter.
Example
//Set the cell value to 2
VP SET NUM VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);2)
//Set the cell value and format it in dollars
VP SET NUM VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);12.356;"_($* #,##0.00_)")See also
VP SET PRINT INFO
VP SET PRINT INFO ( vpAreaName : Text ; printInfo : Object { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area name |
| printInfo | Object | -> | Object containing printing attributes |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET PRINT INFO command defines the attributes to use when printing the vpAreaName.
Pass the name of the 4D View Pro area to print in vpAreaName. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
You can pass an object containing definitions for various printing attributes in the printInfo parameter. To view the full list of the available attributes, see Print Attributes.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet to print (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
The following code will print a 4D View Pro area to a PDF document:
var $printInfo : Object
//declare print attributes object
$printInfo:=New object
//define print attributes
$printInfo.headerCenter:="&BS.H.I.E.L.D. &A Sales Per Region"
$printInfo.firstPageNumber:=1
$printInfo.footerRight:="page &P of &N"
$printInfo.orientation:=vk print page orientation landscape
$printInfo.centering:=vk print centering horizontal
$printInfo.columnStart:=0
$printInfo.columnEnd:=8
$printInfo.rowStart:=0
$printInfo.rowEnd:=24
$printInfo.showGridLine:=True
//Add corporate logo
$printInfo.headerLeftImage:=logo.jpg
$printInfo.headerLeft:="&G"
$printInfo.showRowHeader:=vk print visibility hide
$printInfo.showColumnHeader:=vk print visibility hide
$printInfo.fitPagesWide:=1
$printInfo.fitPagesTall:=1
//print PDF document
VP SET PRINT INFO ("ViewProArea";$printInfo)
//export the PDF
VP EXPORT DOCUMENT("ViewProArea";"Sales2018.pdf";New object("formula";Formula(ALERT("PDF ready!"))))The PDF:
See also
4D View Pro print attributes
VP Convert to picture
VP Get print info
VP PRINT
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES ( rangeObj : Object ; propertyObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range of rows |
| propertyObj | Object | -> | Object containing row properties |
Description
The VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES command applies the attributes defined in the propertyObj to the rows in the rangeObj.
In the rangeObj, pass an object containing a range. If the range contains both columns and rows, attributes are applied only to the rows.
The propertyObj parameter lets you specify the attributes to apply to the rows in the rangeObj. These attributes are:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| height | number | Row height expressed in pixels |
| pageBreak | boolean | True to insert a page break before the first row of the range, else false |
| visible | boolean | True if the row is visible, else false |
| resizable | boolean | True if the row can be resized, else false |
| header | text | Row header text |
Example
You want to change the size of the second row and set the header:
var $row; $properties : Object
$row:=VP Row("ViewProArea";1)
$properties:=New object("height";75;"header";"June")
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES($row;$properties)
See also
VP Get row attributes
VP get column attributes
VP SET ROW ATTRIBUTES
VP SET ROW COUNT
VP SET ROW COUNT ( vpAreaName : Text ; rowCount : Integer { ; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| rowCount | Integer | -> | Number of rows |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET ROW COUNT command defines the total number of rows in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass the total number of rows in the rowCount parameter. rowCount must be greater than 0.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet where the rowCount will be applied (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example
The following code defines five rows in the 4D View Pro area:
VP SET ROW COUNT("ViewProArea";5)
See also
VP Get column count
VP get row-count
VP SET COLUMN COUNT
VP SET SELECTION
VP SET SELECTION ( rangeObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
|rangeObj |Object|->|Range object of cells|
Description
The VP SET SELECTION command defines the specified cells as the selection and the first cell as the active cell.
In rangeObj, pass a range object of cells to designate as the current selection.
Example
$currentSelection:=VP Combine ranges(VP Cells("myVPArea";3;2;1;6);VP Cells("myVPArea";5;7;1;7))
VP SET SELECTION($currentSelection)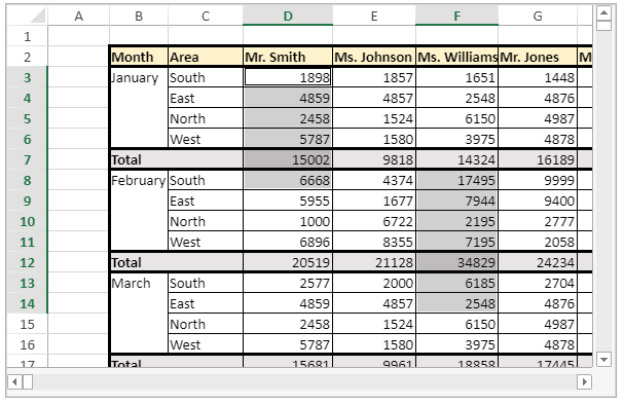
See also
VP Get active cell
VP Get selection
VP RESET SELECTION
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP ADD SELECTION
VP SHOW CELL
VP SET SHEET COUNT
VP SET SHEET COUNT ( vpAreaName : Text ; number : Integer )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| number | Integer | -> | Number of sheets |
Description
The VP SET SHEET COUNT command sets the number of sheets in vpAreaName.
In number, pass a number corresponding to how many sheets the document will contain after the command is executed.
Warning: The command will delete sheets if the previous amount of sheets in your document is superior to the number passed. For example, if there are 5 sheets in your document and you set the sheet count to 3, the command will delete sheets number 4 and 5.
Example
The document currently has one sheet:

To set the number of sheets to 3:
VP SET SHEET COUNT("ViewProArea";3)
See also
VP SET SHEET NAME
VP SET SHEET NAME ( vpAreaName : Text ; name : Text {; sheet: Integer} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| name | Text | -> | New name for the sheet |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Index of the sheet to be renamed |
Description
The VP SET SHEET NAME command renames a sheet in the document loaded in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In name, pass a new name for the sheet.
In sheet, pass the index of the sheet to rename.
Indexing starts at 0.
If no index is passed, the command renames the current sheet.
The new name cannot contain the following characters: *, :, [, ], ?,\,/
The command does nothing if:
- the new name contains forbidden characters
- the new name’s value is blank
- the new name already exists
- the passed index does not exist
Example
Set the third sheet’s name to “Total first quarter”:
VP SET SHEET NAME("ViewProArea";"Total first quarter";2)
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS ( vpAreaName : Text; sheetOptions : Object { ; sheet : Integer} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Object | -> | 4D View Pro area name |
| sheetOptions | Object | -> | Sheet option(s) to set |
| sheet | Object | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET SHEET OPTIONS command allows defining various sheet options of the vpAreaName area.
Pass the name of the 4D View Pro area in vpAreaName. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
Pass an object containing definitions for the options to set in the sheetOptions parameter. To view the full list of the available options, see the Sheet Options paragraph.
In the optional sheet parameter, you can designate a specific spreadsheet (counting begins at 0). If omitted, the current spreadsheet is used by default. You can explicitly select the current spreadsheet with the following constant:
vk current sheet
Example 1
You want to protect all cells except the range C5:D10:
// Activate protection on the current sheet
var $options : Object
$options:=New object
$options.isProtected:=True
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options)
// mark cells C5:D10 as 'unlocked'
VP SET CELL STYLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea";2;4;2;6);New object("locked";False))Example 2
You need to protect your document while your users can resize rows and columns:
var $options : Object
$options:=New object
// Activate protection
$options.isProtected:=True
$options.protectionOptions:=New object
// Allow user to resize rows
$options.protectionOptions.allowResizeRows=True;
// Allow user to resize columns
$options.protectionOptions.allowResizeColumns=True;
// Apply protection on the current sheet
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options)Example 3
You want to customize the colors of your sheet tabs, frozen lines, grid lines, selection background and selection border:
var $options : Object
$options:=New object
// Customize color of Sheet 1 tab
$options.sheetTabColor:="Black"
$options.gridline:=New object("color";"Purple")
$options.selectionBackColor:="rgb(255,128,0,0.4)"
$options.selectionBorderColor:="Yellow"
$options.frozenlineColor:="Gold"
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options;0)
// Customize color of Sheet 2 tab
$options.sheetTabColor:="red"
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options;1)
// Customize color of Sheet 3 tab
$options.sheetTabColor:="blue"
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options;2)Result:
Example 4
You want to hide the grid lines as well as the row and column headers.
var $options : Object
$options:=New object
$options.gridline:=New object()
$options.gridline.showVerticalGridline:=False
$options.gridline.showHorizontalGridline:=False
$options.rowHeaderVisible:=False
$options.colHeaderVisible:=False
VP SET SHEET OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$options)Result:
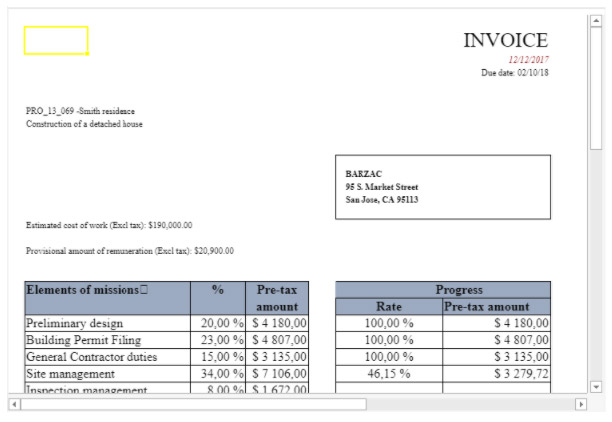
See also
4D View Pro sheet options
VP Get sheet options
VP SET SHOW PRINT LINES
VP SET SHOW PRINT LINES ( vpAreaName : Text {; visible : Boolean}{; sheet : Integer} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| visible | Boolean | -> | Print lines displayed if True (default), hidden if False |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET SHOW PRINT LINES command sets whether to display print preview lines in a spreadsheet..
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In visible, pass True to display the print lines, and False to hide them. True is passed by default.
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
The position of a spreadsheet’s print lines varies according to that spreadsheet’s page breaks.
Example
The following code displays print lines in a document’s second sheet:
VP SET SHOW PRINT LINES("ViewProArea";True;1)
With a page break:
See also
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R7 | Added |
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; column : Integer ; attributes : Object {; sheet : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| column | Integer | -> | Index of the column in the table |
| attributes | Object | -> | Attribute(s) to apply to the column |
| sheet | Integer | -> | Sheet index (current sheet if omitted) |
Description
The VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES command applies the defined attributes to the column in the tableName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In the attributes parameter, pass an object that contains the properties to set:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dataField | text | Table column’s property name in the data context. |
| name | text | Table column’s name. Must be unique in the table. If this name already used by another column, it is not applied and a default name is automaticaly used. |
| formula | text | Sets the formula for each column cell. See Structured Reference Formulas in the SpreadJS documentation |
| footerText | text | Column footer value. |
| footerFormula | text | Column footer formula. |
| filterButtonVisible | boolean | Sets whether the table column’s filter button is displayed (default is Truewhen the table is created). |
In sheet, pass the index of the target sheet. If no index is specified or if you pass -1, the command applies to the current sheet.
Indexing starts at 0.
If tableName is not found or if column is higher than the number of columns, the command does nothing.
Example
You create a table with a data context:
var $context;$options : Object
$context:=New object()
$context.col:=New collection()
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Smith"; "firstname"; "John"; "salary"; 10000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Wesson"; "firstname"; "Jim"; "salary"; 50000))
$context.col.push(New object("name"; "Gross"; "firstname"; "Maria"; "salary"; 10500))
VP SET DATA CONTEXT("ViewProArea"; $context)
//Define the columns for the table
$options:=New object()
$options.tableColumns:=New collection()
$options.tableColumns.push(New object("name"; "Last Name"; "dataField"; "name"))
$options.tableColumns.push(New object("name"; "Salary"; "dataField"; "salary"))
VP CREATE TABLE(VP Cells("ViewProArea"; 1; 1; 2; 3); "PeopleTable"; "col"; $options)
Then you want to insert a column with data from the data context and hide some filter buttons:
//insert a column
VP INSERT TABLE COLUMNS("ViewProArea"; "PeopleTable"; 1; 1)
var $param : Object
$param:=New object()
// Bind the column to the firstname field from the datacontext
$param.dataField:="firstname"
// Change the default name of the column to "First name"
// and hide the filter button
$param.name:="First Name"
$param.filterButtonVisible:=False
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES("ViewProArea"; "PeopleTable"; 1; $param)
// Hide the filter button of the first column
VP SET TABLE COLUMN ATTRIBUTES("ViewProArea"; "PeopleTable"; 0; \
New object("filterButtonVisible"; False))
See also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP Find table
VP Get table column attributes
VP RESIZE TABLE
VP SET TABLE THEME
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v19 R8 | Added |
VP SET TABLE THEME ( vpAreaName : Text ; tableName : Text ; options : cs.ViewPro.TableTheme )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| tableName | Text | -> | Table name |
| options | cs.ViewPro.TableTheme | -> | Table theme properties to modify |
Description
The VP SET TABLE THEME command modifies the current theme of the tableName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area and in tableName, the name of the table to modify.
In the options parameter, pass an object of the cs.ViewPro.TableTheme class that contains the theme properties to modify.
Example 1
You want to set a predefined theme to a table:
var $param : cs.ViewPro.TableTheme
$param:=cs.ViewPro.TableTheme.new()
$param.theme:="medium2"
VP SET TABLE THEME("ViewProArea"; "myTable"; $param)Example 2
You want to have this alternate column rendering:
var $param : cs.ViewPro.TableTheme
$param:=cs.ViewPro.TableTheme.new()
// Enable the band column rendering
$param.bandColumns:=True
$param.bandRows:=False
// Create the theme object with header and column styles
$param.theme:=cs.ViewPro.TableThemeOptions.new()
var $styleHeader; $styleColumn; $styleColumn2 : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
$styleHeader:=cs.ViewPro.TableStyle.new()
$styleHeader.backColor:="Gold"
$styleHeader.foreColor:="#03045E"
$param.theme.headerRowStyle:=$styleHeader
$styleColumn1:=cs.ViewPro.TableStyle.new()
$styleColumn1.backColor:="SkyBlue"
$styleColumn1.foreColor:="#03045E"
$param.theme.firstColumnStripStyle:=$styleColumn1
$styleColumn2:=cs.ViewPro.TableStyle.new()
$styleColumn2.backColor:="LightCyan"
$styleColumn2.foreColor:="#03045E"
$param.theme.secondColumnStripStyle:=$styleColumn2
VP SET TABLE THEME("ViewProArea"; "myTable"; $param)
See also
VP CREATE TABLE
VP Get table theme
VP SET TEXT VALUE
VP SET TEXT VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; textValue : Text { ; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| textValue | Text | -> | Text value to set |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of value |
Description
The VP SET TEXT VALUE command assigns a specified text value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The textValue parameter specifies a text value to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the textValueparameter.
Example
VP SET TEXT VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);"Test 4D View Pro")See also
VP SET TIME VALUE
VP SET TIME VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; timeValue : Text { ; formatPattern : Text } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| timeValue | Text | -> | Time value to set |
| formatPattern | Text | -> | Format of value |
Description
The VP SET TIME VALUE command assigns a specified time value to a designated cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The timeValue parameter specifies a time expressed in seconds to be assigned to the rangeObj.
The optional formatPattern defines a pattern for the timeValueparameter.
Example
//Set the value to the current time
VP SET TIME VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);Current time)
//Set the value to a specific time with a designated format
VP SET TIME VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);?12:15:06?;vk pattern long time)See also
Cell Format
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE
VP SET VALUE
VP SET VALUE
VP SET VALUE ( rangeObj : Object ; valueObj : Object )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| valueObj | Object | -> | Cell values and format options |
Description
The VP SET VALUE command assigns a specified value to a designated cell range.
The command allows you to use a generic code to set and format the types of values in rangeObj, whereas other commands, such as VP SET TEXT VALUE and VP SET NUM VALUE, reduce the values to specific types.
In rangeObj, pass a range of the cell(s) (created for example with VP Cell or VP Column) whose value you want to specify. If rangeObj includes multiple cells, the value specified will be repeated in each cell.
The parameter valueObj is an object that includes properties for the value and the format to assign to rangeObj. It can include the following properties :
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | Integer, Real, Boolean, Text, Date, Null | Value to assign to rangeObj(except- time). Pass null to erase the content of the cell. |
| time | Real | Time value (in seconds) to assign to rangeObj |
| format | Text | Pattern for value/time property. For information on patterns and formatting characters, please refer to the Cell Format paragraph. |
Example
//Set the cell value as False
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);New object("value";False))
//Set the cell value as 2
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);New object("value";2))
//Set the cell value as $125,571.35
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);New object("value";125571.35;"format";"_($* #,##0.00_)"))
//Set the cell value as Hello World!
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;2);New object("value";"Hello World!"))
//Set the cell value as current date
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";4;2);New object("value";Current date))
//Set the cell value as current hour
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";5;2);New object("time";Current hour))
//Set the cell value as specific date and time
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;9);New object("value";!2024-12-18!);"time";?14:30:10?;"format";vk pattern full date time))
//Erase cell content
VP SET VALUE(VP Cell("ViewProArea";3;9);New object("value";Null))See also
Cell Format
VP Get values
VP SET VALUE
VP SET BOOLEAN VALUE
VP SET DATE TIME VALUE
VP SET FIELD
VP SET FORMULA
VP SET NUM VALUE
VP SET TEXT VALUE
VP SET TIME VALUE
VP SET VALUES
VP SET VALUES ( rangeObj : Object ; valuesCol : Collection )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
| valuesCol | Collection | -> | Collection of values |
Description
The VP SET VALUES command assigns a collection of values starting at the specified cell range.
In rangeObj, pass a range for the cell (created with VP Cell) whose value you want to specify. The cell defined in the rangeObj is used to determine the starting point.
- If rangeObj is not a cell range, only the first cell of the range is used.
- If rangeObj includes multiple ranges, only the first cell of the first range is used.
The valuesCol parameter is two-dimensional:
- The first-level collection contains subcollections of values. Each subcollection defines a row. Pass an empty collection to skip a row.
- Each subcollection defines cell values for the row. Values can be Integer, Real, Boolean, Text, Date, Null, or Object. If the value is an object, it can have the following properties:PropertyTypeDescriptionvalueInteger, Real, Boolean, Text, Date, NullValue in the cell (except- time)timeRealTime value (in seconds)
Example
$param:=New collection
$param.push(New collection(1;2;3;False)) //first row, 4 values
$param.push(New collection) //second row, untouched
$param.push(New collection(4;5;Null;"hello";"world")) // third row, 5 values
$param.push(New collection(6;7;8;9)) // fourth row, 4 values
$param.push(New collection(Null;New object("value";Current date;"time";42))) //fifth row, 1 value
VP SET VALUES(VP Cell("ViewProArea";2;1);$param)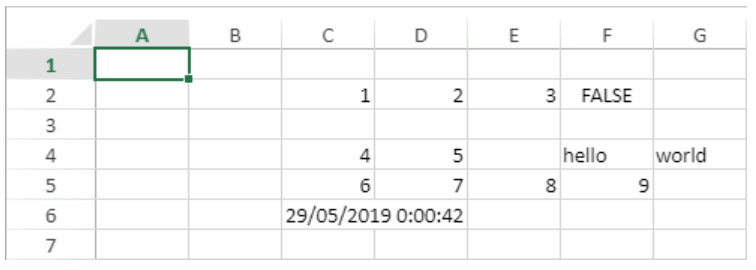
See also
VP Get formulas
VP Get value
VP Get Values
VP SET FORMULAS
VP SET VALUE
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS ( vpAreaName : Text ; optionObj : Object)
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
| optionObj | Object | -> | Object containing the workbook options to be set |
Description
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS sets the workbook options in vpAreaName.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area.
In optionObj, pass the workbook options to apply to vpAreaName.
If optionObj is empty, the command does nothing.
Modified workbook options are saved with the document.
The following table lists the available workbook options:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allowUserDragMerge | boolean | The drag merge operation is allowed (select cells and drag the selection to merge cells) |
| allowAutoCreateHyperlink | boolean | Enables automatic creation of hyperlinks in the spreadsheet. |
| allowContextMenu | boolean | The built-in context menu can be opened. |
| allowCopyPasteExcelStyle | boolean | Styles from a spreadsheet can be copied and pasted to Excel, and vice-versa. |
| allowDynamicArray | boolean | Enables dynamic arrays in worksheets |
| allowExtendPasteRange | boolean | Extends the pasted range if the pasted range is not enough for the pasted data |
| allowSheetReorder | boolean | Sheet reordering is allowed |
| allowUndo | boolean | Undoing edits is allowed. |
| allowUserDeselect | boolean | Deselecting specific cells from a selection is allowed. |
| allowUserDragDrop | boolean | Drag and drop of range data is allowed |
| allowUserDragFill | boolean | Drag fill is allowed |
| allowUserEditFormula | boolean | Formulas can be entered in cells |
| allowUserResize | boolean | Columns and rows can be resized |
| allowUserZoom | boolean | Zooming (ctrl + mouse wheel) is allowed |
| autoFitType | number | Content is formatted to fit in cells, or cells and headers. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk auto fit type cell 0The content autofits cellsvk auto fit type cell with header 1The content autofits cells and headers |
| backColor | string | A color string used to represent the background color of the area, such as “red”, “#FFFF00”, “rgb(255,0,0)”, “Accent 5”. The initial backgroundcolor is hidden when a backgroundImage is set. |
| backgroundImage | string / picture / file | Background image for the area. |
| backgroundImageLayout | number | How the background image is displayed. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk image layout center 1In the center of the area.vk image layout none 3In the upper left corner of the area with its original size.vk image layout stretch 0Fills the area.vk image layout zoom 2Displayed with its original aspect ratio. |
| calcOnDemand | boolean | Formulas are calculated only when they are demanded. |
| columnResizeMode | number | Resize mode for columns. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk resize mode normal 0Use normal resize mode (i.e remaining columns are affected)vk resize mode split 1Use split mode (i.e remaining columns are not affected) |
| copyPasteHeaderOptions | number | Headers to include when data is copied to or pasted. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk copy paste header options all headers3Includes selected headers when data is copied; overwrites selected headers when data is pasted.vk copy paste header options column headers 2Includes selected column headers when data is copied; overwrites selected column headers when data is pasted.vk copy paste header options no headers0Column and row headers are not included when data is copied; does not overwrite selected column or row headers when data is pasted.vk copy paste header options row headers1Includes selected row headers when data is copied; overwrites selected row headers when data is pasted. |
| customList | collection | The list for users to customize drag fill, prioritize matching this list in each fill. Each collection item is a collection of strings. See on GrapeCity’s website. |
| cutCopyIndicatorBorderColor | string | Border color for the indicator displayed when the user cuts or copies the selection. |
| cutCopyIndicatorVisible | boolean | Display an indicator when copying or cutting the selected item. |
| defaultDragFillType | number | The default drag fill type. Available values : ConstantValueDescriptionvk auto fill type auto 5Automatically fills cells. vk auto fill type clear values 4Clears cell values.vk auto fill type copycells 0Fills cells with all data objects, including values, formatting, and formulas.vk auto fill type fill formatting only 2Fills cells only with formatting.vk auto fill type fill series 1Fills cells with series. vk auto fill type fill without formatting 3Fills cells with values and not formatting. |
| enableAccessibility | boolean | Accessibility support is enabled in the spreadsheet. |
| enableFormulaTextbox | boolean | The formula text box is enabled. |
| grayAreaBackColor | string | A color string used to represent the background color of the gray area , such as “red”, “#FFFF00”, “rgb(255,0,0)”, “Accent 5”, and so on. |
| highlightInvalidData | boolean | Invalid data is highlighted. |
| iterativeCalculation | boolean | Enables iterative calculation. See on Grapecity’s website. |
| iterativeCalculationMaximumChange | numeric | Maximum amount of change between two calculation values. |
| iterativeCalculationMaximumIterations | numeric | Number of times the formula should recalculate. |
| newTabVisible | boolean | Display a special tab to let users insert new sheets. |
| numbersFitMode | number | Changes display mode when date/number data width is longer than column width. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk numbers fit mode mask0Replace data content with “###” and shows tipvk numbers fit mode overflow 1Display data content as a string. If next cell is empty, overflow the content. |
| pasteSkipInvisibleRange | boolean | Paste or skip pasting data in invisible ranges: False (default): paste dataTrue: Skip pasting in invisible rangesSee Grapecity’s docs for more information on invisible ranges. |
| referenceStyle | number | Style for cell and range references in cell formulas. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk reference style A1 0Use A1 style.vk reference style R1C1 1Use R1C1 style |
| resizeZeroIndicator | number | Drawing policy when the row or column is resized to zero. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk resize zero indicator default 0Uses the current drawing policy when the row or column is resized to zero.vk resize zero indicator enhanced 1Draws two short lines when the row or column is resized to zero. |
| rowResizeMode | number | The way rows are resized. Available values are the same as columnResizeMode |
| scrollbarAppearance | number | Scrollbar appearance. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk scrollbar appearance mobile1Mobile scrollbar appearance.vk scrollbar appearance skin (default)0Excel-like classic scrollbar appearance. |
| scrollbarMaxAlign | boolean | The scroll bar aligns with the last row and column of the active sheet. |
| scrollbarShowMax | boolean | The displayed scroll bars are based on the entire number of columns and rows in the sheet. |
| scrollByPixel | boolean | Enable precision scrolling by pixel. |
| scrollIgnoreHidden | boolean | The scroll bar ignores hidden rows or columns. |
| scrollPixel | integer | Decides scrolling by that number of pixels at a time when scrollByPixel is true. The final scrolling pixels are the result of scrolling delta * scrollPixel. For example: scrolling delta is 3, scrollPixel is 5, the final scrolling pixels are 15. |
| showDragDropTip | boolean | Display the drag-drop tip. |
| showDragFillSmartTag | boolean | Display the drag fill dialog. |
| showDragFillTip | boolean | Display the drag-fill tip. |
| showHorizontalScrollbar | boolean | Display the horizontal scroll bar. |
| showResizeTip | number | How to display the resize tip. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk show resize tip both 3Horizontal and vertical resize tips are displayed.vk show resize tip column 1Only the horizontal resize tip is displayed.vk show resize tip none 0No resize tip is displayed.vk show resize tip row 2Only the vertical resize tip is displayed. |
| showScrollTip | number | How to display the scroll tip. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk show scroll tip both 3Horizontal and vertical scroll tips are displayed.vk show scroll tip horizontal 1Only the horizontal scroll tip is displayed.vk show scroll tip none No scroll tip is displayed.vk show scroll tip vertical 2Only the vertical scroll tip is displayed. |
| showVerticalScrollbar | boolean | Display the vertical scroll bar. |
| tabEditable | boolean | The sheet tab strip can be edited. |
| tabNavigationVisible | boolean | Display the sheet tab navigation. |
| tabStripPosition | number | Position of the tab strip. Available values: ConstantValueDescriptionvk tab strip position bottom 0Tab strip position is relative to the bottom of the workbook.vk tab strip position left 2Tab strip position is relative to the left of the workbook.vk tab strip position right 3Tab strip position is relative to the right of the workbook.vk tab strip position top 1Tab strip position is relative to the top of the workbook. |
| tabStripRatio | number | Percentage value (0.x) that specifies how much of the horizontal space will be allocated to the tab strip. The rest of the horizontal area (1 – 0.x) will allocated to the horizontal scrollbar. |
| tabStripVisible | boolean | Display the sheet tab strip. |
| tabStripWidth | number | Width of the tab strip when position is left or right. Default and minimum is 80. |
| useTouchLayout | boolean | Whether to use touch layout to present the Spread component. |
Example
To set the allowExtendpasteRange option in “ViewProArea”:
var $workbookOptions : Object
$workbookOptions:= New Object
$workbookOptions.allowExtendPasteRange:=True
VP SET WORKBOOK OPTIONS("ViewProArea";$workbookOptions)See also
VP SHOW CELL
VP SHOW CELL ( rangeObj : Object { ; vPos : Integer; hPos : Integer } )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rangeObj | Object | -> | Range object |
|vPos |Integer|->|Vertical view position of cell or row| |hPos |Integer|->|Horizontal view position of cell or row|
Description
The VP SHOW CELL command vertically and horizontally repositions the view of the rangeObj.
In rangeObj, pass a range of cells as an object to designate the cells to be viewed. The view of the rangeObj will be positioned vertically or horizontally (i.e., where rangeObj appears) based on the vPos and hPos parameters. The vPos parameter defines the desired vertical position to display the rangeObj, and the hPos parameter defines the desired horizontal position to display the rangeObj.
The following selectors are available:
| Selector | Description | Available with vPos | Available with hPos |
|---|---|---|---|
vk position bottom |
Vertical alignment to the bottom of cell or row. | X | |
vk position center |
Alignment to the center. The alignment will be to the cell, row, or column limit according to the view position indicated:Vertical view position – cell or rowHorizontal view position – cell or column | X | X |
vk position left |
Horizontal alignment to the left of the cell or column | X | |
vk position nearest |
Alignment to the closest limit (top, bottom, left, right, center). The alignment will be to the cell, row, or column limit according to the view position indicated:Vertical view position (top, center, bottom) – cell or row Horizontal view position (left, center, right) – cell or column | X | X |
vk position right |
Horizontal alignment to the right of the cell or column | X | |
vk position top |
Vertical alignment to the top of cell or row | X |
This command is only effective if repositioning the view is possible. For example, if the rangeObj is in cell A1 (the first column and the first row) of the current sheet, repositioning the view will make no difference because the vertical and horizontal limits have already been reached (i.e., it is not possible to scroll any higher or any more to the left). The same is true if rangeObj is in cell C3 and the view is repositioned to the center or the bottom right. The view remains unaltered.
Example
You want to view the cell in column AY, row 51 in the center of the 4D View Pro area:
$displayCell:=VP Cell("myVPArea";50;50)
// Move the view to show the cell
VP SHOW CELL($displayCell;vk position center;vk position center)Result:
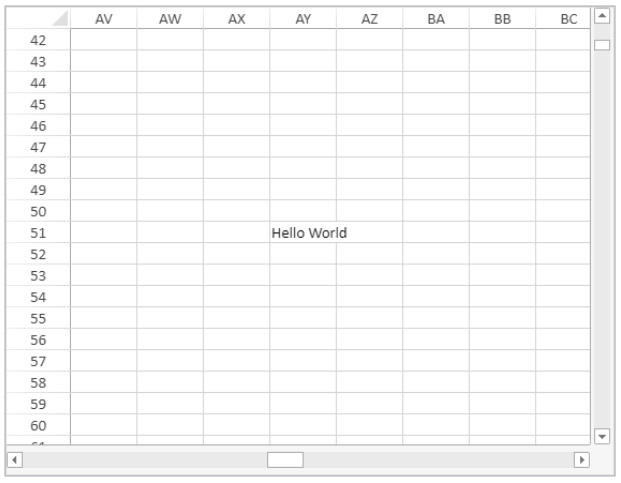
The same code with the vertical and horizontal selectors changed to show the same cell positioned at the top right of the 4D View Pro area:
$displayCell:=VP Cell("myVPArea";50;50)
// Move the view to show the cell
VP SHOW CELL($displayCell;vk position top;vk position right)Result:
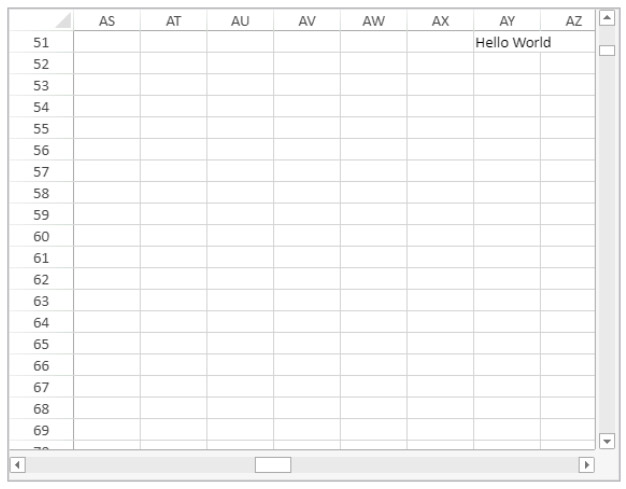
See also
VP ADD CELL
VP Get active cell
VP Get selection
VP RESET SELECTION
VP SET ACTIVE CELL
VP SET SELECTION
VP SUSPEND COMPUTING
VP SUSPEND COMPUTING ( vpAreaName : Text )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| vpAreaName | Text | -> | 4D View Pro area form object name |
Description
The VP SUSPEND COMPUTING command stops the calculation of all formulas in vpAreaName. This command is useful when you want to suspend calculations in this 4D View Pro area so you can manually make modifications to formulas without encountering errors before you’ve finished making the changes.
The command pauses the calculation service in 4D View Pro. Formulas that have already been calculated remain unchanged, however any formulas added after VP SUSPEND COMPUTINGcommand is executed are not calculated.
In vpAreaName, pass the name of the 4D View Pro area. If you pass a name that does not exist, an error is returned.
The 4D View Pro calculation service maintains a counter of suspend/resume actions. Therefore, each execution of
VP SUSPEND COMPUTINGcommand must be balanced by a corresponding execution of theVP RESUME COMPUTINGcommand. Any formula impacted by modifications made while calculations are suspended will be recalculated when the command is executed.
Example
You’ve added two buttons to the form so that the user can suspend/resume calculations:
The Suspend Computing button code:
//pause calculations while users enter information
If(FORM Event.code=On Clicked)
VP SUSPEND COMPUTING("ViewProArea")
End ifIf(FORM Event.code=On Clicked)
VP RESUME COMPUTING("ViewProArea")
End ifSee also
VP RECOMUTE FORMULAS
VP RESUME COMPUTING
Classes
The following classes can be used in 4D View Pro.
LineBorder
.color
.color : Text
The .color property is the color of the border. Default = black.
.style
.style : Integer
The .style property is the style of the border. Default = empty.
TableColumn
.dataField
.dataField : Text
The .dataField property contains the table column’s property name in the data context.
.formatter
.formatter : Text
The .formatter property contains the table column’s formatter.
.name
.name : Text
The .name property contains the table column’s name (mandatory).
TableOptions
.allowAutoExpand
.allowAutoExpand : Boolean
The .allowAutoExpand property indicates whether to expand columns or rows of the table when values are added in empty adjacent cells. Default = True
.bandColumns
.bandColumns : Boolean
The .bandColumns property indicates whether to display an alternating column style. Default = False
.bandRows
.bandRows : Boolean
The .bandRows property indicates whether to display an alternating row style. Default = True
.highlightLastColumn
.highlightLastColumn : Boolean
The .highlightLastColumn property indicates whether to highlight the last column. Default = False
.highlightFirstColumn
.highlightFirstColumn : Boolean
The .highlightFirstColumn property indicates whether to highlight the first column. Default = False
.showFooter
.showFooter : Boolean
The .showFooter property indicates whether to display a footer. Default = False
.showHeader
.showHeader : Boolean
The .showHeader property indicates whether to display a header. Default = True
.showResizeHandle
.showResizeHandle : Boolean
The .showResizeHandle property indicates whether to display the resize handle for tables that don’t have a source. Default = False
.tableColumns
.tableColumns : Collection
The .tableColumns property is a collection of cs.ViewPro.TableColumn objects used to create the table’s columns.
.theme
.theme : cs.ViewPro.TableThemeOptions
The .theme property defines a table theme. Can also be a text (name of a native SpreadJS theme).
See the native SpreadJS themes.
.useFooterDropDownList
.useFooterDropDownList : Boolean
The .useFooterDropDownList property indicates whether to use a dropdown list in footer cells that calculate the total value of a column. Default = False
TableStyle
.backColor
.backColor : Text
The .backColor property is the background color of the table.
.forecolor
.forecolor : Text
The .forecolor property is the foreground color of the table.
.font
.font : Text
The .font property is the font name (see Fonts and text) of the table.
.textDecoration
.textDecoration : Integer
The .textDecoration property is the text decoration of the table (see Fonts and text).
.borderLeft
.borderLeft : cs.ViewPro.LineBorder
The .borderLeft property is the left border line of the table .
.borderRight
.borderRight : cs.ViewPro.LineBorder
The .borderRight property is the right border line of the table .
.borderBottom
.borderBottom : cs.ViewPro.LineBorder
The .borderBottom property is the bottom border line of the table .
.borderHorizontal
.borderHorizontal : cs.ViewPro.LineBorder
The .borderHorizontal property is the horizontal border line of the table .
.borderVertical
.borderVertical : cs.ViewPro.LineBorder
The .borderVertical property is the vertical border line of the table .
TableTheme
.bandRows
.bandRows : Boolean
The .bandRows property indicates whether to display an alternating row style.
.bandColumns
.bandColumns : Boolean
The .bandColumns property indicates whether to display an alternating column style.
.highlightLastColumn
.highlightLastColumn : Boolean
The .highlightLastColumn property indicates whether to highlight the last column.
.highlightFirstColumn
.highlightFirstColumn : Boolean
The .highlightFirstColumn property indicates whether to highlight the first column.
.theme
.theme : cs.ViewPro.TableThemeOptions
.theme : Text
The .theme property defines a table theme. If Text: name of a native SpreadJS theme.
TableThemeOptions
.firstColumnStripSize
.firstColumnStripSize : Integer
The .firstColumnStripSize property is the size of the first alternating column. Default=1
.firstColumnStripStyle
.firstColumnStripStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .firstColumnStripStyle property is the style of the first alternating column.
.firstFooterCellStyle
.firstFooterCellStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .firstFooterCellStyle property is the style of the first footer cell. “highlightFirstColumn” must be true.
.firstHeaderCellStyle
.firstHeaderCellStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .firstHeaderCellStyle property is the style of the first header cell. “highlightFirstColumn” must be true.
.firstRowStripSize
.firstRowStripSize : Integer
The .firstRowStripSize property is the size of the first alternating column. Default=1.
.firstRowStripStyle
.firstRowStripStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .firstRowStripStyle property is the first alternating row style.
.footerRowStyle
.footerRowStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .footerRowStyle property is the default style of the footer area.
.headerRowStyle
.headerRowStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .headerRowStyle property is the default style of the header area.
.highlightFirstColumnStyle
.highlightFirstColumnStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .highlightFirstColumnStyle property is the style of the first column. “highlightFirstColumn” must be true.
.highlightLastColumnStyle
.highlightLastColumnStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .highlightLastColumnStyle property is the style of the last column. “highlightLastColumn” must be true.
.lastFooterCellStyle
.lastFooterCellStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .lastFooterCellStyle property is the style of the last footer cell. “highlightLastColumn” must be true.
.lastHeaderCellStyle
.lastHeaderCellStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .lastHeaderCellStyle property is the style of the last header cell. “highlightLastColumn” must be true.
.name
.name : Text
The .name property is the name of a native SpreadJS theme.
.secondColumnStripSize
.secondColumnStripSize : Integer
The .secondColumnStripSize property is the size of the second alternating column. Default=1
.secondColumnStripStyle
.secondColumnStripStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .secondColumnStripStyle property is the style of the second alternating column.
.secondRowStripSize
.secondRowStripSize : Integer
The .secondRowStripSize property is the size of the second alternating column. Default=1.
.secondRowStripStyle
.secondRowStripStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .secondRowStripStyle property is the second alternating row style.
.wholeTableStyle
.wholeTableStyle : cs.ViewPro.TableStyle
The .wholeTableStyle property is the default style of the data area.
Advanced programming with Javascript
A 4D View Pro Area is a Web Area form object that uses the embedded web rendering engine. As such, it behaves just like any other web area, and you can get it to execute Javascript code by calling the WA Evaluate Javascript 4D command.
Since 4D View Pro is powered by the SpreadJS spreadsheet solution, you can also call SpreadJS Javascript methods in 4D View Pro areas.
Hands-on example: Hiding the Ribbon
Since 4D View Pro is a web area, you can select a webpage element and modify its behavior using Javascript. The following example hides the spreadJS Ribbon:
//Button's object method
var $js; $answer : Text
$js:="document.getElementsByClassName('ribbon')[0].setAttribute('style','display: none');"
$js+="window.dispatchEvent(new Event('resize'));"
$answer:=WA Evaluate JavaScript(*; "ViewProArea"; $js)Calling SpreadJS Javascript methods
You can tap into the SpreadJS library of Javascript methods and call them directly to control your spreadsheets.
4D has a built-in Utils.spread property that gives access to the spreadsheet document (also called workbook) inside the 4D View Pro area, making it simpler to call the SpreadJS Workbook methods.
Example
The following code undoes the last action in the spreadsheet:
WA Evaluate JavaScript(*; "ViewProArea"; "Utils.spread.undoManager().undo()")4D View Pro Tips repository
4D-View-Pro-Tips is a GitHub repository that contains a project full of useful functions, allowing to manage floating pictures, sort columns or rows, create a custom culture, and much more! Feel free to clone it and experiment with the project.
You can review our Blog and YouTube channel for additional information and resources on SapphireOne ERP, CRM and Business Accounting software.